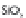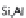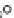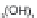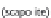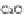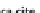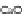Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 1.10
Carbonate rock.
The minerals that are stable in medium to high grade metamorphism are in bold; those stable only at
low grade metamorphism are in normal font.
The primary free carbonate will become abundant when the initial pro-
portion of carbonates was larger: Such rocks abundant carbonates are
marbles. The presence of a small proportion of clay, quartz and other
minerals in the initial rock is reflected by the presence of calcic silicates,
which remain minors in front of the carbonates. This carbonate is usu-
ally calcite. Dolomite, if it was present initially, often reacts, rather than
calcite, with silica and silicates to form magnesium silicates like talc,
tremolite, phlogopite, diopside, forsterite and/or spinel)
+
calcite.
Metamorphism transforms a rock originally composed almost only of
carbonate, with a very small proportion of silica clays, into a nearly
pure marble.
5
Hydrothermal rocks
are endogenous rocks formed through the circula-
tion of a (usually hydrated) fluid: either by direct precipitation (quartz
veins, mineral veins, alpine veins with axinite, epidote, albite) or by
transformation by these fluids of preexisting rocks. The metasomatic
process, with introduction and leaching of elements, leads to the forma-
tion of specific rocks that are often almost monomineralic: secondary
dolomites, chloritites, albitites ...
white mica, result from the
leaching of alkali feldspar and are developed mostly at the expense of acid
Greisens
are mainly formed of quartz
+