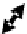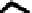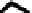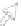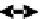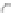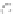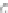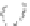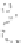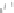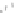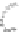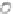Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
accessory for the original interface of the equipment. In this case the new interface,
completely deported, can be specific to the requirements of the user (Figure 6.5c).
Wearable
computer
E
qu
i
pm
ent
Wearable
computer
Wearable
computer
Eq
uipm
ent
Eq
uipm
ent
Use
Use
Use
(a) No direct communication
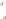
(b) One way communication
(c) Two way communication
Figure 6.5.
Types of communication between the computerized
accessory and the equipment
6.8.
Mobile Learning
from e-Truck and e-Bus
perspectives
Among the activities which can take place in the
e-Truck
and
e-Bus
context,
Mobile Learning
holds a unique place, as it can involve both transport professionals
and users.
Mobile Learning (M-Learning)
is a form of learning which uses mobile
devices; it is the result of the development of mobile technologies, including
wireless networks and the evolution of learning methods. One of the most
significant definitions of
M-Learning
is “any kind of learning which occurs when
the learner is not static, in a specified location, or learning which occurs when the
learner takes advantage of the learning possibilities offered by mobile technologies”
[OMA 03]. Without going into more detail faced with the different
M-Learning
taxonomies
[MEY 06], we can only separate
M
-
Learning
into two categories
according to whether or not the context is taken into account. The first category
considers the learning activity as totally independent of the localization of the
learner and the context in which he involves, only taking into account the possibility
of using mobile devices with a view to learning (in the cafeteria, during lesson
breaks, etc.). On the other hand, our second category indicates a learning activity in
relation to the location (physical, geographical, logical) of the learner and the
context in which he evolves. We focus on this second category of
M
-
learning
where
the context plays an important part (the driver learns to use and repair his truck, he
manages distribution while respecting constraints imposed by a customer).
Contextualized
M-learning
targets the consideration of the situation and
Just
in
time
Learning
,
Learning
by
Doing
and the
Learning & Doing
approach. Among the
previously introduced
M-Learning
situations, we made a distinction between
situated and non-situated
M-Learning
. The former is directly linked to the context in
which the learner finds himself, the latter is independent from this. In transport, we
find these two versions of
M-Learning
, as we will see.