Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
y
(
A
,
B
,0)
A
a
(
a
,
b
,0)
B
θ
b
s
φ
x
(a)
P
(0,0,1)
y
Q
(0,0,
z
)
z
θ
s
φ
x
(b)
z
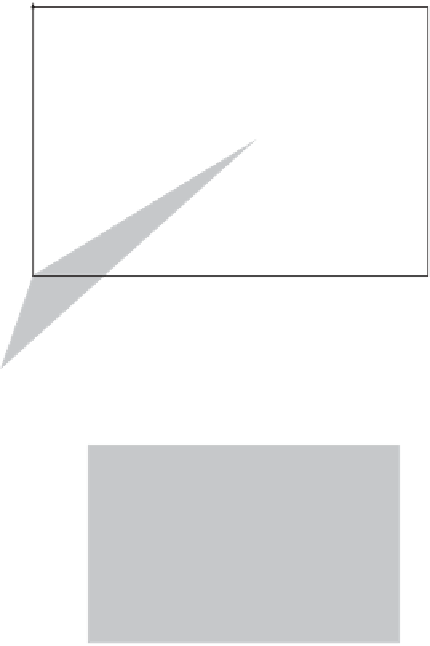
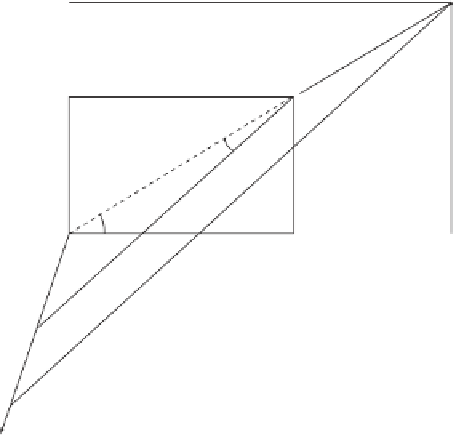
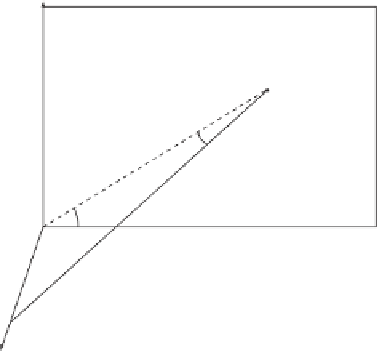
Figure 2.14: Oblique Projections.
3. A cabinet projection. It is defined as the case where the projection angle is
63
.
43
◦
, which implies
s
= cot(63
.
43
◦
)=1
/
2. All edges and segments perpendicular to
the projection plane have shrink factors of 1
/
2.
Figure 2.14b shows how
φ
and
θ
are independent. For a given projection angle
θ
,
it is possible to assign
φ
any value by rotating the triangle in the figure. In practice,
this means that an object can be projected several times, with different values of
φ
but
with the same projection angle
θ
. Such projections may give all the necessary visual
information about the object while having the same shrink factors.
Shrink: To become constricted from heat, moisture, or cold.
(A typical dictionary definition)










Search WWH ::

Custom Search