Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
4
3
2
1
1
3
4
2
Figure 4.17: Four Circles and Lines.
Exercise 4.6:
Search the mathematical literature or the Internet (or just think about
this) to find another anallagmatic curve.
L
Q
*
Q
P
P
*
O
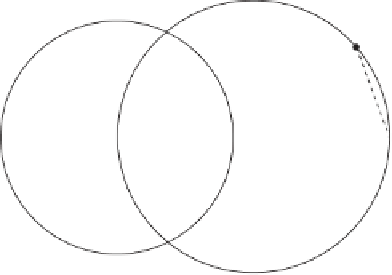
Figure 4.18: Circular Inversion of a Line.
Here is a proof of feature 4. Figure 4.18 shows a line
L
that does not pass through
the origin. Consequently, there must be a perpendicular to
L
from the origin. The point
where this perpendicular meets
L
is denoted
P
and its projection is denoted
P
∗
.We
now select another arbitrary point
Q
on
L
and denote its projection
Q
∗
. It is obvious
that
OP
OP
∗
=1and
OQ
OQ
∗
=1,soweconcludethat
OP/OQ
∗
=
OQ/OP
∗
.This
·
·
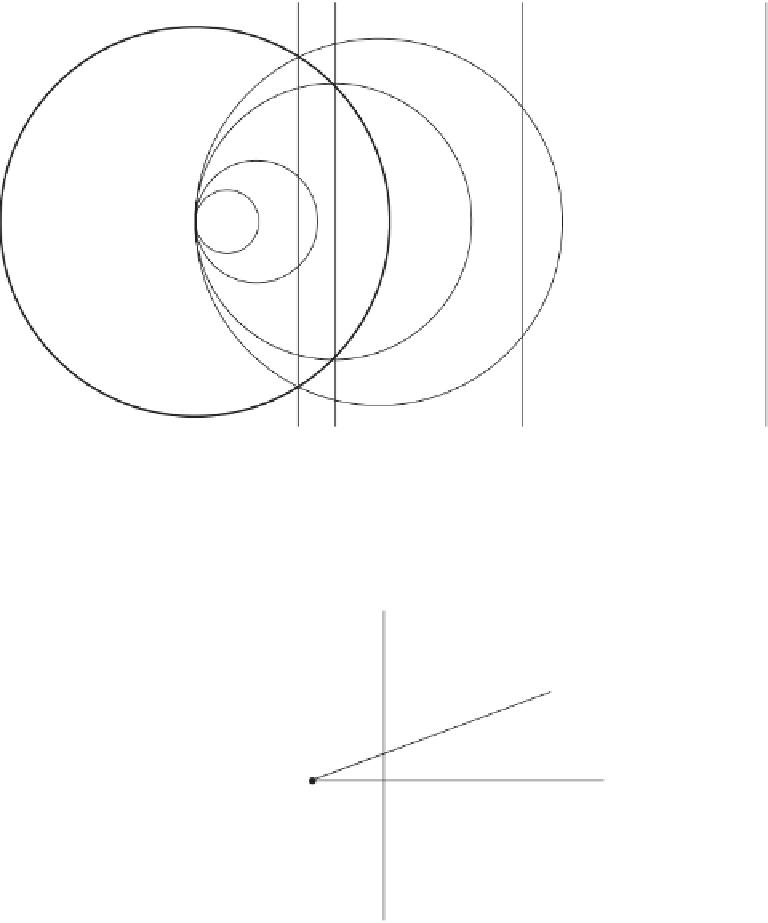


Search WWH ::

Custom Search