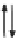Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
of the policy representation to the rest of the system. This can be achieved
in a number of ways. One approach is to interpret the policy representation
at run time, so that it can be retrieved from a suitable repository (as, for
example, in directory enabled networking [59, 96]); this allows changes to be
made by updating the repository since the various system components will
retrieve the new version next time they need to interpret the policy. Another
alternative is to provide the policy as a plug-in object within a suitable com-
ponent management framework, or as a service identified by a reference that
can be rebound dynamically when necessary.
One well-known architecture for applying policies is defined by the IETF,
and involves the identification of sets of control points for each class of policy.
There are two kinds of control point (see, for example, figure 10.3).
access
control
PEP
admission
control
PEP
account
manager
video
client
network
control
pause /
rewind
video
store
access
control
PDP
admission
control
PDP
load
monitor
access
policies
admission
policies
FIGURE 10.3: The use of policy execution points and policy decision points
to control policies in a streaming video server.
The policy execution points (PEPs) are points at which choices have to be
made based on the policy in question. When a decision is needed, the PEP
communicates details of the request to a policy decision point (PDP) which
interprets or otherwise consults the policy and determines what the outcome
should be. It then returns the result to the PEP, which behaves accordingly,
permitting or prohibiting the request. The advantage of this structure is that
the policy value is interpreted by comparatively few PDPs, which may be
serving very many more PEPs, each associated with individual fine-grained
resources.
The PEP/PDP structure assumes that there is a need for controlled en-
forcement of a policy whenever it applies. This is what is known as a pes-
simistic policy enforcement approach. The system is constructed in such a way
that the enforcement points make it impossible to violate the policy. However,
this is not the only way of handling enforcement. There is another approach,
called optimistic policy enforcement, in which the policy is published and the
system then monitored, possibly on a sampling basis, to check that the policy
is being observed. If the policy is seen to have been violated, some corrective