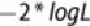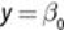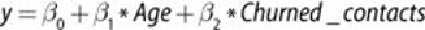Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Call:
glm(formula = Churned ˜ Age + Churned_contacts,
family = binomial(link = "logit"), data = churn_input)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.4599 -0.5214 -0.1960 -0.0736 3.3671
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 3.502716 0.128430 27.27 <2e-16 ***
Age -0.156551 0.004085 -38.32 <2e-16 ***
Churned_contacts 0.381857 0.027297 13.99 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' '
1
(Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 8387.3 on 7999 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 5359.2 on 7997 degrees of freedom
AIC: 5365.2
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 6
For this final model, the entire summary output is provided. The output offers
several values that can be used to evaluate the fitted model. It should be noted that
the model parameter estimates correspond to the values provided in
Equation 6.11
Deviance and the Pseudo-R
2
In logistic regression, deviance is defined to be , where L is the
maximized value of the likelihood function that was used to obtain the parameter
estimates. In the R output, two deviance values are provided. The
null deviance
is the value where the likelihood function is based only on the intercept term (
). The
residual deviance
is the value where the likelihood function is
based on the parameters in the specified logistic model, shown in
Equation 6.12
.
A metric analogous to R
2
in linear regression can be computed as shown in