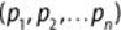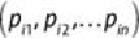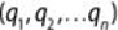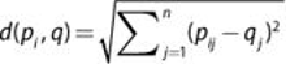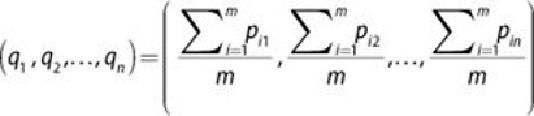Database Reference
In-Depth Information
c. Repeat until the algorithm reaches the final answer.
Convergence is reached when the computed centroids do not change or
the centroids and the assigned points oscillate back and forth from one
iteration to the next. The latter case can occur when there are one or more
points that are equal distances from the computed centroid.
To generalize the prior algorithm to n dimensions, suppose there are M
objects, where each object is described by n attributes or property values
. Then object
i
is described by for
i
= 1,2,…, M.
In other words, there is a matrix with M rows corresponding to the M
objects and n columns to store the attribute values. To expand the earlier
process to find the k clusters from two dimensions to n dimensions, the
following equations provide the formulas for calculating the distances and
the locations of the centroids for n ≥ 1.
For a given point,
p
i
, at and a centroid,
q
, located at
, the distance,
d
, between
p
i
and
q
, is expressed as shown in
The centroid,
q,
of a cluster of m points,
, is calculated as
shown in
Equation 4.4
.
4.4