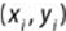Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Image Processing
Video is one example of the growing volumes of unstructured data being collected.
Within each frame of a video, k-means analysis can be used to identify objects in
the video. For each frame, the task is to determine which pixels are most similar to
each other. The attributes of each pixel can include brightness, color, and location,
the x and y coordinates in the frame. With security video images, for example,
successive frames are examined to identify any changes to the clusters. These
newly identified clusters may indicate unauthorized access to a facility.
Medical
Patient attributes such as age, height, weight, systolic and diastolic blood
pressures, cholesterol level, and other attributes can identify naturally occurring
clusters. These clusters could be used to target individuals for specific preventive
measures or clinical trial participation. Clustering, in general, is useful in biology
for the classification of plants and animals as well as in the field of human genetics.
Customer Segmentation
Marketing and sales groups use k-means to better identify customers who have
similar behaviors and spending patterns. For example, a wireless provider may
look at the following customer attributes: monthly bill, number of text messages,
data volume consumed, minutes used during various daily periods, and years as a
customer. The wireless company could then look at the naturally occurring clusters
and consider tactics to increase sales or reduce the customer
churn rate
, the
proportion of customers who end their relationship with a particular company.
4.2.2 Overview of the Method
To illustrate the method to find k clusters from a collection of M objects with
n attributes, the two-dimensional case (n = 2) is examined. It is much easier
to visualize the k-means method in two dimensions. Later in the chapter, the
two-dimension scenario is generalized to handle any number of attributes.
Because each object in this example has two attributes, it is useful to consider
each object corresponding to the point , where x and y denote the two
attributes and i = 1, 2 … M. For a given cluster of m points (m M), the point that
corresponds to the cluster's mean is called a
centroid
. In mathematics, a centroid
refers to a point that corresponds to the center of mass for an object.