Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Bulk Liquid
Biofilm
2. Cell synthesis
and respiration
2. Cell synthesis
and respiration
1. Substrate
Mass Transport
1. Substrate
Mass Transport
E
anode
E
anode
3. Electrical
potential gradient
3. Electrical
potential gradient
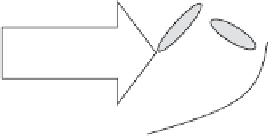
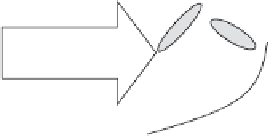
Fig. 1.5 General schematic for the three main processes that occur at the biofilm anode of an
MFC and control the current density and anode potential losses: (1) mass transport brings
electrons from the substrate into the biofilm, (2) cells partition electrons into different ways,
and (3) electrical potential controls bacterial respiration, while the conduction of electrons
from the biofilm anode into the electrode depends on the gradient of the electrical potential
limitation by electron-donor diffusion and utilization (Section 1.2.2.1). Then, we
modify the biofilm kinetic model using concepts of electrochemistry so that we
can explore the electrical potential limitation in the MFC anode (Section 1.2.2.2).
1.2.2.1 Limitation by Electron-Donor Diffusion and Utilization
In the following case, the anode current density is only limited by the substrate
flux into the biofilm. In order to obtain the substrate flux, J
s
, we must establish a
mass balance within the biofilm that takes into consideration substrate diffusion
and utilization. By combining Fick's law of diffusion with Monod-type kinetics
of substrate consumption, Rittmann and McCarty (2001) estimate the substrate
flux into the biofilmwith known concentrations at both boundaries of the biofilm
(i.e., S
s
at the biofilm/liquid interface and S
w
at the biofilm attachment wall) [32]:
2
K
þ
S
w
K
þ
S
s
J
s
¼
2q
max
X
f
D
f
S
s
S
w
þ
K ln
(1
:
8)
in which, q
max
is the maximum specific rate of substrate utilization (M
substrate
/
(M
biomass
*T)), X
f
is the biomass density within the biofilm (M
biomass
/Vol), D
f
is
the substrate molecular diffusion coefficient in the biofilm (Area/T), and K is
the substrate concentration at which r
ut
= 0.5q
max
X
f
(M
substrate
/Vol)
The maximum flux obtainable for a given S
s
occurs when S
w
=0. This is
referred to as a deep biofilm, for which
1
2
K
K
þ
S
s
J
s, deep
¼
2q
max
X
f
D
f
S
s
þ
K ln
(1
:
9)