Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
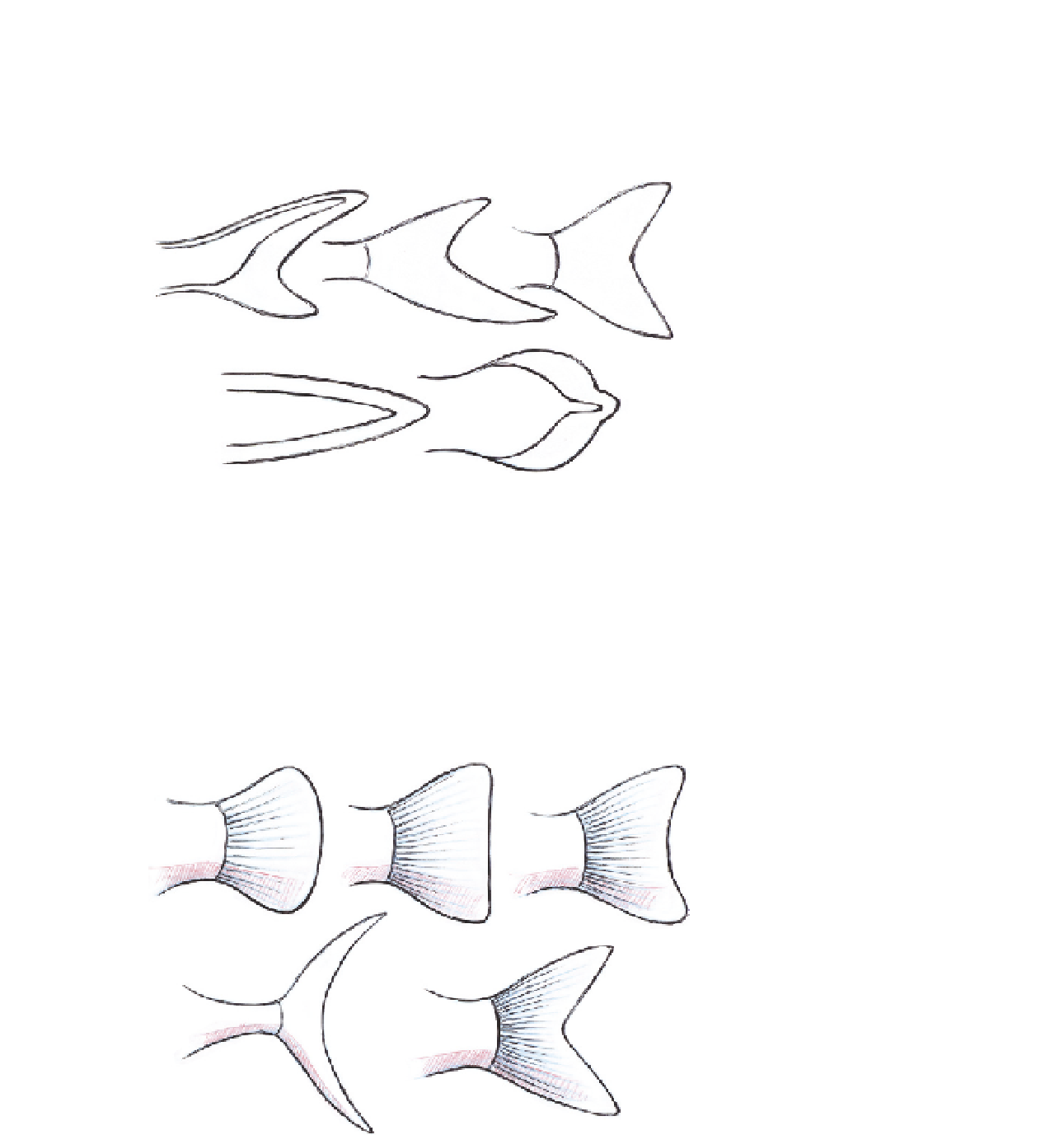
There are various shapes of caudal fin. Asymmetrical caudal fins that have
vertebrae extending into the larger lobe are known as
heterocercal
. In sharks
the upper lobe is longer, or
epicercal
, while the tails of fish that have longer
lower lobes are known as
hypocercal
.
(a)
(b)
(c)
FIG 4.73
The tail or cordal fins vary
from species to species. a: Heterocer-
cal. b: Hypocercal.
c: Homocercal. d: Protocercal.
e: Diphycercal.
(d)
(e)
However, most fish have tails in which the vertebrae do not extend into a lobe
and the tail fins are more or less symmetrical; these are termed
homocercal
.
There is still a good deal of variation in the shape of caudal fins that conform
to this homocercal structure.
Rounded caudal fins are almost completely rounded at the end as in the
barramundi
Lates calcarifer
. Truncated caudal fins have an almost vertical edge,
as can be seen in the Atlantic salmon
Salmo salar
. Forked caudal fins may end in
two prongs of roughly equal lengths, as in the roach
Rutilus rutilus
.
Emarginate
(a)
(b)
(c)
FIG 4.74
The different shapes of
caudal fins. a: Rounded. b: Truncated.
c: Emarginate. d: Lunate. e: Forked.
(d)
(e)