Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
×
10
-3
6
M
=
32
5
T
=
500
K
4
3
M
=
4
2
M
=
2
1
0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
Speed,
u
( m s
-1
)
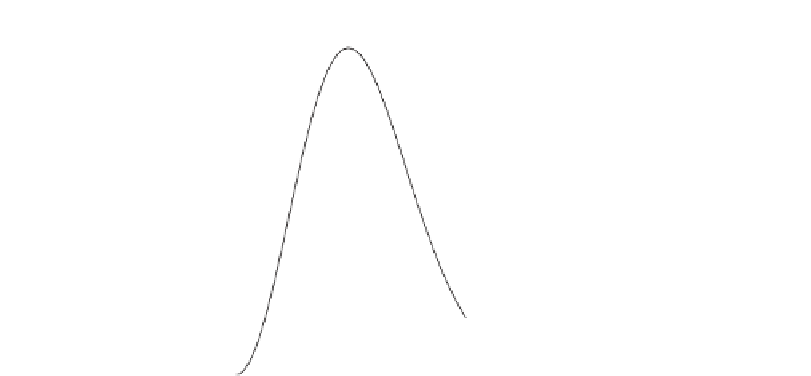
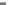
Figure 12.19
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds for hydrogen (
M
=
2), helium (
M
=
4), and oxygen
2kms
−
1
), H
2
and He will quickly be lost while CO
2
will take longer
to leave the gravity field. In contrast, only H
2
will rapidly be lost from the Earth's atmosphere.
(
M
=
32). On the Moon (
u
=
Miss
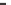
Miss
Hit
Miss
Hit
Figure 12.20
Collisions within gas. A molecule will sweep a cylinder of radius twice its radius. The mean free
path is the mean distance between successive collisions.
than the escape velocity does not bump into any other molecule before being set free from
gravity, it is lost. Otherwise, it is very likely to lose energy in collisions with the more
abundant slow molecules and must wait until it gets a chance of another good push to be
taken further.
What about the mean free path? Let us assume that our molecule is a sphere with radius
r
and a footprint (cross-section) of 4
other molecule in a cylinder of twice its radius. The number of collisions d
N
is equal to
π