Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Continent
Ocean
Bottom of the
lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Crust
Upper
mantle
ol + pyr + gr
40 km
rg + gr
410 km
660 km
pv + mw
Lower
mantle
2890 km
D"
FeNi
(liq)
Outer
core
5150 km
FeNi
(sol)
Inner
core
6370 km
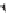
Figure 11.1
The internal structure of the Earth determined by the propagation of seismic waves from
earthquakes. Essential minerals of the mantle are garnet (gr), magnesio-wüstite (mw),
olivine (ol), perovskite (pv), pyroxene (pyr), and ringwoodite (rg).
Mid-ocean ridge
basalts (MORB)
Orogenic
volcanism
(andesites)
Oceanic
crust
Conduction
Advection
Dissipation
Continental
crust
Oceanic
lithospheric
mantle
Trench
Subcontinental
lithospheric
mantle
Asthenosphere
Mid-ocean-
ridge
Subduction
zone
Figure 11.2
The essential components of plate tectonics: mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones, and rigid
lithospheric plates. Oceanic crust is in gray. The three mechanisms of heat loss through the surface
are shown: conduction through the lithosphere, advection of magmas at mid-ocean ridges, and
dissipation of the potential energy of sinking plates at subduction zones, where plates bend.