Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
10
−
8
Anorthite
10
−
10
10
−
12
10
−
14
Albite
10
−
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
pH
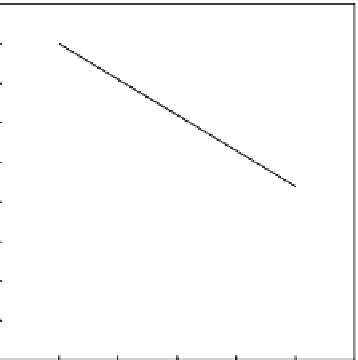
Figure 7.11
Dependence of albite and anorthite weathering rates on pH. Acid waters dissolve feldspars faster
than neutral waters. These rates typically increase by a factor of ten when temperature increases
by 25
◦
C.
of H
+
. Quite commonly, rain-water pH values fall in a range of 4-6. Acid waters have
the greatest erosion potential because abundant H
+
displaces the major soluble ions (Na
+
,
K
+
,Ca
2
+
,Mg
2
+
) constituting the rock-forming minerals. Once normalized to surface area
and after establishment of steady state, most mineral dissolution rates
R
may adequately
be described by the equation:
ln
R
=
ln
R
0
+
n
pH
(7.47)
where
R
0
and
n
are constant for a specified mineral. Temperature dependence of the dis-
solution rate is very critical: warm climates promote chemical erosion. This dependence
takes the usual form:
E
RT
=
−
ln
R
A
(7.48)
where
A
is a constant and
E
the activation energy of this particular reaction. Values of
n
between 0 and
1 are common, while
E
usually falls between the activation energy of
ionic diffusion in solution and the energy required to break the silicate bond. Weathering
rates typically increase by a factor of ten when temperature increases by 25
◦
C. The pH-
dependence property of the weathering rates is illustrated for feldspars in
Fig. 7.11
.
The major features of river chemistry may be summarized with a small number of
parameters. After subtraction of cyclic ions, the remainder of the dissolved load of fresh
water can be divided into carbonate alkalinity (from dissolution of silicates by the reactions
described above or from redissolution of limestone), sulfate and chloride from dissolution
of evaporites, and silica from dissolution of silicates (
Fig. 7.12
). These quantities vary
greatly with the site where water erodes the soil. In addition to the dissolved load, rivers
transport abundant mineral (clay and iron hydroxides) and organic colloids.
−