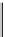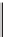Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Geological age (Ma)
300
290
280
270
260
1200
U-Pb zircon
1000
Sm-Nd and Lu-Hf
garnet
K-Ar
amphibole
Rb-Sr
muscovite
800
K-Ar
biotite
600
Rb-Sr
biotite
K-Ar
K-feldspar
400
Fission
tracks
U-He
apatite
200
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
Time (million years)
Figure 5.5
Hypothetical changes in temperature during the uplift and erosion of land after an orogenic
period. The example is for a rock whose zircons crystallized 300 million years ago. The different
closure temperatures of the various clocks and the ages define a temperature-time curve.
retentive for argon as soon as ambient temperature drops below 342
◦
C. Closure tempera-
ture depends mostly on grain size. Error bars on closure temperatures are of the order of
50-80
◦
C.
Closure temperatures of different chronometers for specific minerals can be calculated
from diffusion experiments.
Figure 5.5
shows a hypothetical curve constructed to show
cooling after the formation of mountain ranges in a given area. If equilibration pres-
sure is known, all of this information forms the pressure-temperature-time (
PTt
) path
of exhumation of the orogen, an essential tool in modern tectonics. This same tool is also
much used in petroleum exploration to determine the thermal evolution of sedimentary
basins and the probability of temperatures suitable for oil formation being attained locally.
The concept of closure is not restricted to chronometers but applies to most assemblages
of co-existing phases and begs the question of what mineral thermometers and barometers
(barothermometry) actually record. Let us consider a rock made of four different miner-
in a percolating hydrothermal or metamorphic fluid. At high temperatures, all the miner-
als exchange material among themselves and with the fluid in order to keep the overall
energy of the system to a minimum (equilibration). When temperature drops below the
closure temperature of any particular mineral, exchange between this mineral and the rest