Java Reference
In-Depth Information
A new
Item
entity corresponding to the record being added is first instantiated in the
ad-
dItem
method. All of the relevant
Item
entity data to be saved into the database, such
as the item title and description, is then populated with the data passed in by the user.
Seller
entity. The related seller is retrieved using the
EntityManager
's
find
meth-
od and set as a field of the
Item
entity. The
persist
method is then invoked to save the
ded to create new entity records in the database and not update existing ones. This means
that you should make sure the identity or primary key of the entity to be persisted doesn't
already exist in the database. If you try to persist an entity and the primary key already
exists in the database, an
EntityExistsException
may be thrown either when the
persist
method is called or when the transaction is being committed.
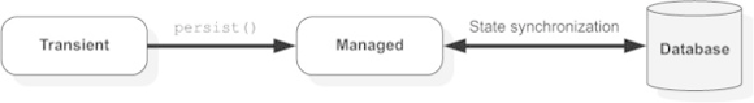
Figure 10.6. Invoking the
persist
method on the
EntityManager
interface makes an entity instance managed.
When the transaction commits, the entity state is synchronized with the database.
If you try to persist an entity that violates another of the database's integrity constraints
(such as an additional unique constraint), the persistence provider will throw an appropriate
subclass of
javax.persistence.PersistenceException
, which wraps the
database exception.
As noted earlier, the
persist
method also causes the entity to become managed as
soon as the method returns. The
INSERT
statement (or statements) that creates the record
corresponding to the entity isn't necessarily issued immediately. For transaction-scoped
EntityManager
s, the statement is typically issued when the enclosing transaction is
about to commit. In the example, this means the SQL statements are issued when the
addItem
method returns. For extended-scoped (or application-managed)
EntityMan-
ager
s, the
INSERT
statement is usually issued right before the
EntityManager
is
closed. The
INSERT
statement can also be issued at any point when the
EntityMan-
ager
is flushed.