Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
were inherited by the descendants of the common ancestor on higher
branches of the tree.
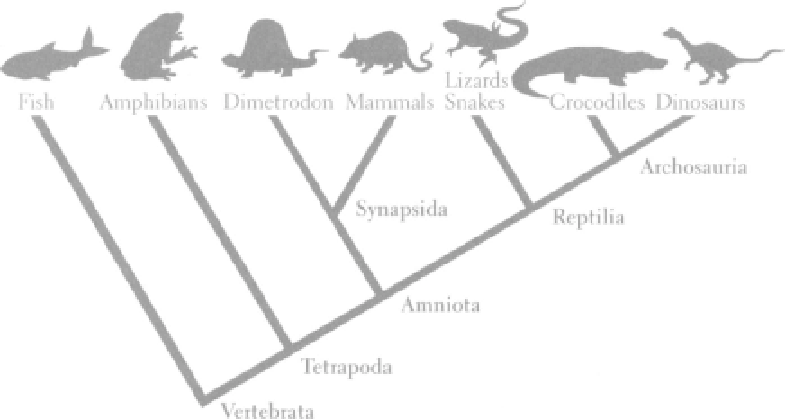
For example, some characteristics are shared by a large number of
animals. Fish, frogs, dinosaurs, and humans all have a backbone
composed of vertebrae. Thus, they all belong to the group of animals
called vertebrates, which constitutes a major limb on the family tree
of animals. The backbone is thought to have evolved in the very
first vertebrate, or the common ancestor of the group. Then, all of its
descendants, including humans, inherited a backbone from that
common ancestor. Other characteristics are shared by a smaller num-
ber of animals within the vertebrate group. For instance, frogs,
dinosaurs, and humans have four limbs (arms and legs) with bony
wrists, ankles, fingers, and toes, so these animals belong to a subgroup
of vertebrates called tetrapods, which means "four-footed." Tetrapods
represent a smaller branch on the limb of the tree that contains all
the vertebrates. Again, four limbs originally evolved in the ancestor of
all tetrapods, and all the descendants of that common ancestor,
including humans, inherited some version of its four limbs.
Since having a backbone is more widespread among animals than
having four limbs—for example, since fish have backbones but lack
limbs—the backbone is thought to have evolved before the limbs did.
Genealogical relationships of the major groups of vertebrate animals. Birds
arc included within dinosaurs.