Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.1
The Inside of a Web
bble
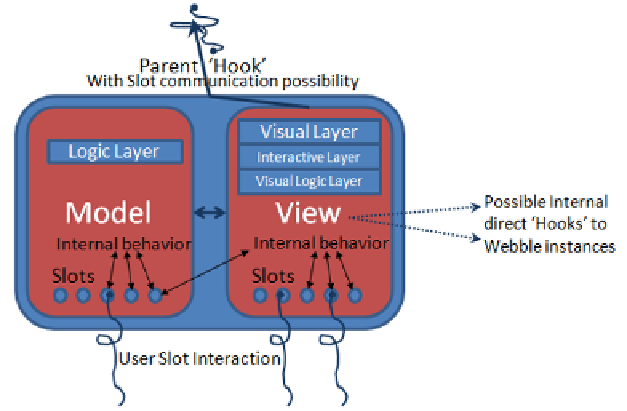
As seen in figure 1, a Web
model is the business logic
the Webble is displayed or
is all related to display and
lated logic.
bble is defined by two parts, the model and the view. T
part of the Webble, that handles matters unrelated to h
how the user interacts with it. The view on the other h
d user interaction, which should only contain interface
The
how
hand
re-
Fig. 1.
A virtual cr
ross section of a primitive Webble as described below
These two parts are cod
and when combined and pu
a primitive Webble. Being
place; The possibility to co
commonly known as a pa
number of children but onl
Webbles and bind Webble
Each Webble has slots, bot
gurable properties of a We
both internally and externa
nect. Beyond these few spe
ble or contain any type of fe
Every Webble can also b
neric Webble behavior con
(ab)use when being used fo
When a Webble is saved
includes all valuable meta
links. Rather small files tha
ded the traditional way in a classic programming langu
ublished to the platform becomes a Webble, also known
a Webble means that some specific characteristics are
onnect to other Webbles in a hierarchical structure, m
arent - child relationship. A Webble can have unlimi
ly one parent. This allows the user to easier organize
es that work together in intuitive groups and sub grou
th within the model as well is in the view. Slots are co
ebble but they are also the basic communication chann
ally as is demonstrated in figure 2 where the user can c
ecific trademarks a Webble may look in any way imagi
eatures.
be duplicated, deleted and saved, as well as having its
nfigured in order to protect it from unwanted, unintentio
or a specific purpose.
d, online or locally, it is stored plainly as an XML file, t
data, slot values, child-parent relations and needed U
at can easily be shared with the world.
uage
n as
e in
most
ited
the
ups.
nfi-
nels
con-
ina-
ge-
onal
that
URI