Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
But meme media allow for much more than just plugging building blocks into
each other. They support the propagation of data via slot connections [47] and
enable direct execution [13]. Both features do not seem so particularly relevant
to the few cases discussed so far within the present paper.
Among the numerous ideas and principles of collaborative learning, there is
the “divide and conquer” meme: set up some task, divide it into two subtasks,
let two (groups of) learners solve these tasks independently, and synthesize a
solution to the original problem by combination of the solutions to the subtasks.
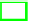
Fig. 6.
Encapsulation of the “Divide and Conquer” Collaborative Learning Meme
For a particular learning domain, the different nodes of the storyboard cutout
shown in figure 6 may have different implementations. Within some first variant,
-
'Formulate a Task' is a teacher's duty,
-
'Divide the Task...'is anactivityofthe wholegroup,
-
'WorkingonsomeSolution...' isa taskofseparateindividuals orgroups,
-
'Combining the Two Solutions' is an activity of the whole group again.
Within a second variant of implementing the visualization on display in figure 6,
only the two 'Working on some Solution ...' nodes representhuman activities.
All the others have a certain computational meaning. Just for illustration, there
may be some task generator (maybe, reading tasks from a database), a certain
procedure of dividing tasks into subtasks, and some program merging solutions
of subtasks into solutions of the original tasks.
The second variant sketched does illuminate that the edges of a storyboard
may have different semantics (see [26] for more in-depth discussions including
the semantics of nodes). Edges do not only represent the flow of control. They
specify data flow as well. The flow of data between nodes with some operational
semantics may be fully automated. Assume you plug one node into another one.
In this way, some slots are connected. Data flow from the slot of one meme media
object to the corresponding slot of the other one according to some predefined
direction. Those settings of data flow may be adjusted by hand, if necessary.
In fig. 6, e.g., the rightmost node runs a merging algorithm when data are put in.
When discussing didactic concepts in [25] (see also section 4 on exploratory
learning in [30]), there has been investigated some particular idea usefull for
learning algorithms, their reach, strengths, weaknesses, and details of behavior.