Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
6.1.3.6
Ring-shaped magnets enable oscillatory measurements
Most NdFeB-based magnetic tweezers employ opposed pairs of cubic magnets that
typically allow for only unidirectional pulling, and therefore do not allow for oscil-
latory measurements around a stress-free state. We have recently shown that for a
ring-shaped NdFeB magnet, the gradient of the magnetic field changes sign along
the symmetry axis, allowing both pushing and pulling forces to be generated (
Lin &
Valentine, 2012b
). This makes ring magnets ideal for use in oscillatory microrheology
measurements, in which frequency-dependent viscoelastic parameters are easily
obtained. The overall design is similar to that of simplemagnetic tweezers, but the cube
magnet array is replaced with a single NdFeB ring magnet of square cross section (i.e.,
inner radius of 0.125 in., outer radius of 0.375 in., and thickness of 0.125 in., and max-
imum remanent field
B
r
¼
1.32 T). With this geometry, we observe two force reversals
as a function of distance along the
z
-axis (
Fig. 6.7
). One transition occurs within a mil-
limeter of the front face of the magnet, and a second occurs at an axial distance of
4 mm. This second, gentler transition is a good candidate for stable manipulation
of beads around a zero-force position, a requirement for many applications of oscilla-
tory microrheology. To achieve cyclical actuation, the servo motor that vertically lifts
the magnet array is driven using a triangle waveform. We find that bead displacement
primarily occurs along the
z
-axis, with smaller lateral
x
-
y
motions. Coupling between
300
200
100
0
-
100
2
6
10
14
18
Separation distance (mm)
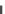
FIGURE 6.7
Calibration curve for ring magnet-based magnetic tweezers device showing force reversals.
The main figure shows the calibration curve of force versus separation distance between
the magnet assembly and the sample plane. Data are obtained by measuring the velocity at
which 4.5
m diameter beads moved through a glycerol solution of known viscosity under
force. Arrow indicates magnet position at which the force gently reverses sign. F
m
<
0 indicates
pushing forces whereas F
>
0 indicates pulling. Inset shows the magnetic field lines
generated by a ring magnet.
Adapted from
Lin and Valentine (2012b)
. Reprinted with permission from the
American Institute of Physics, Copyright 2012.