Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
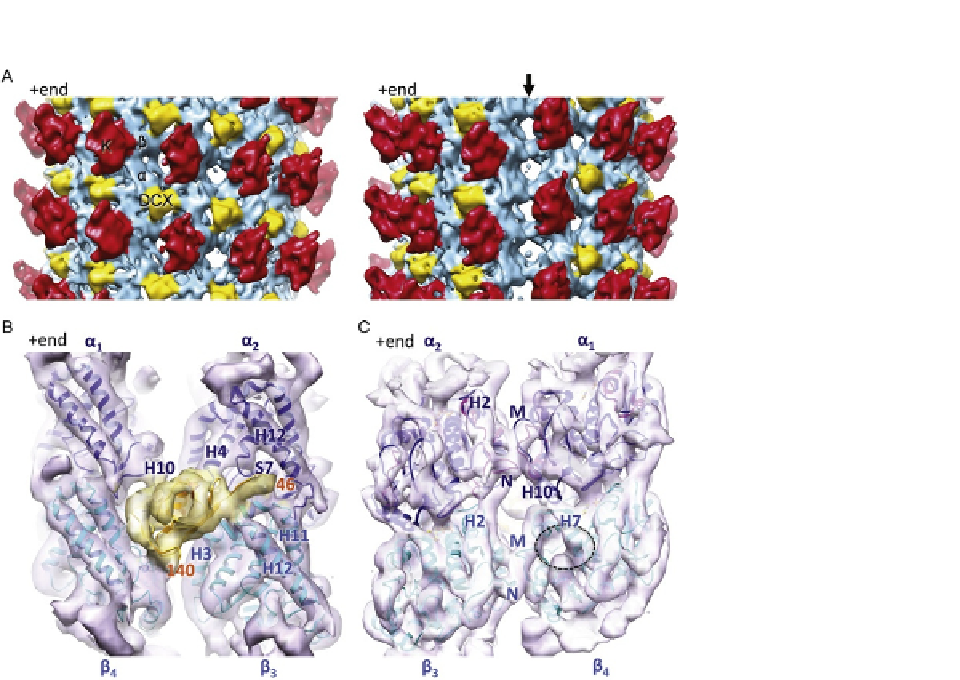
FIGURE 3.5
Structure of DCX-K-MTs determined using Chuff. (A) Asymmetric reconstruction of DCX-K-
MTs (
Fourniol et al., 2010
; EMDB ID 1787). Side views, 180
apart, of a cryo-EM
reconstruction of DCX-MTs decorated with kinesin motor domain, low-pass filtered with a
13
˚
cut-off, density thresholded at 3
. Each kinesin motor domain (red) binds one
ab-tubulin heterodimer (blue). DCX (yellow) binds at the interface between four tubulin
dimers. The density for DCX is visible in the interprotofilament valleys all around the MT up
to a threshold of 5
s
; arrow, right panel).
(B) Averaged view of DCX-binding site with the pseudo-atomic coordinates docked within the
cryo-EM envelope. Tubulin secondary structural elements are labeled in blue, and the
N- and C-terminal residues of the docked DCX coordinates are labeled in orange (EMDB ID
1788, PDB ID 2XRP; N-DC in gold, alpha-tubulin in blue, and beta-tubulin in cyan).
(C) Averaged view of the inside surface of the DCX-MT reconstruction, highlighting the
inter-pf lateral contacts that form in the MT wall. The empty paclitaxel-binding pocket
is indicated (dotted circle). The chimeric lateral loops used to generate the a-tubulin
pseudo-atomic model are shown in pink and tubulin secondary structural elements and loops
are labeled in blue.
s
, except at the seam (no density above 3
s