Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
Brain extracts
P2
Adult
P2
Adult
P2
Adult
P2
Adult
Ponceau S
a
-Tubulin
b
-Tubulin
GT335
5
m
g/ml
1
m
g/ml
0.5
m
g/ml
0.25
m
g/ml
GT335 dilution
B
Brain extracts
1
´
2
´
4
´
8
´
Relative load
P2
Adult
P2
Adult
P2
Adult
P2
Adult
Ponceau S
a
-Tubulin
12G10
a
-Tubulin
GT335
0.5
m
g/ml
b
-Tubulin
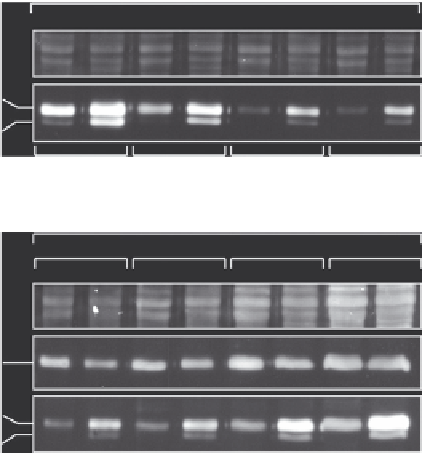
FIGURE 16.3
Impact of sample and antibody concentration on the assessment of tubulin modification
levels by immunoblot. Comparative immunoblot analysis of protein extracts from 2 days
old and adult mouse brain. The samples have been resolved on 10% gels allowing for
separation of a- and b-tubulin. (A) Equal amounts of the two samples were separated on
SDS-PAGE, and following the transfer, incubated with a different dilution of the GT335
antibody (glutamylation): 5, 1, 0.5, and 0.25 mg/ml. At higher concentrations of GT335,
differences in modification levels of a-tubulin are not detected, while they are obvious at lower
antibody concentrations. Differences in glutamylation in b-tubulin, which is less modified
in brain (
Audebert et al., 1994
), are still detectable at higher GT335 concentrations. Ponceau
S staining of the blot membranes indicates loading. (B) Increasing amounts of samples were
loaded and revealed with highly diluted GT335 (0.5 mg/ml). Similarly to (A), differences in
glutamylation levels are faint at higher sample load, though the tubulin bands still look
very distinct and might thus not suggest an overload of the sample. Ponceau S and 12G10
(a-tubulin) indicate total load and a-tubulin levels.
Piperno & Fuller, 1985
). The antibody detects acetylated tubulin in most species
tested so far.
16.2.1.2
Tyrosination/detyrosination/
2-tubulin
Tyrosinated
a
-tubulin is recognized by the YL1/2 rat monoclonal antibody (Millipore
#MAB1964;
Cumming et al., 1984; Kilmartin et al., 1982
). This antibody was raised
against purified yeast tubulin and thus recognizes the C-terminal -EEF and -EEY
sequences on
a
-tubulin.
D