Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
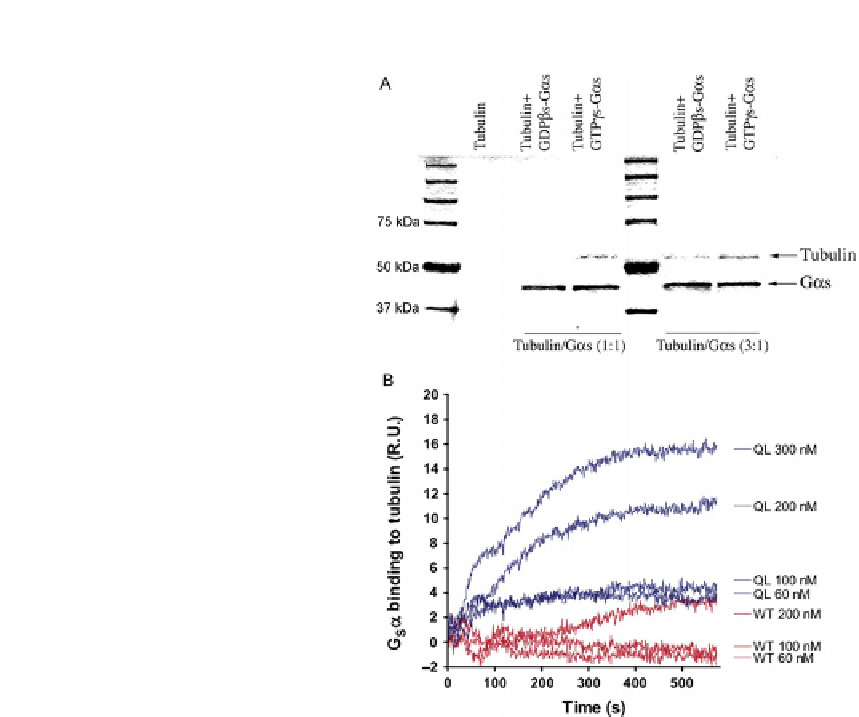
FIGURE 12.2
In vitro determination of the association between tubulin and Gsa. (A) Coprecipitation of Gsa
and tubulin. His-Gas-GTPgS(5mg) or His-Gas-GDPbS(5mg) was incubated with tubulin
for 2 h at room temperature followed by pull down using nickel-agarose beads. After
separation by SDS-PAGE, the gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. (B) Sensorgrams
representing the surface plasmon resonance analysis of the interaction between immobilized
tubulin and GsaQL or GsaWT. The concentration series used were 60, 100, and 200 nM.
GsaQL binds to tubulin with k
a
¼
10
4
M
1
s
1
, k
d
¼
10
3
s
1
, and K
D
¼
5
100 nM.
This research was originally published by
Dave et al. (2011)
5
ligand) and buffer is also injected into each flow cell. In addition, BSA injected into the
flow cells failed to detectably bind tubulin.
12.1.1.4
Peptide array membrane analysis
To identify the Gs
a
regions that specifically interact with tubulin, we use peptide
array analysis. Peptides corresponding to the primary Gs
a
sequence as well as the
Gt
a
sequence are covalently attached to a cellulose-based membrane. As Gt
a
(trans-
ducin) has been shown to not interact with tubulin despite significant sequence and