Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
stimulus waveform over the pulse duration. It describes how steeply the capacitor dis-
charges into the patient's body and gives an indication of how much of the stored energy
is delivered to the tissues. Tilt is dependent on the
RC
time constant (device capacitance
times the impedance of the transthoracic discharge pathway).
Duration
refers to the extent
of the de
fi
brillation waveform. Commonly, duration is in the range 8 to 40 ms.
Bare-Bones De
fi
brillator
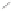
Figure 8.31 shows a damped sine waveform de
brillator. A transformer T1 steps up the
power line voltage to a high voltage (a few kilovolts). Capacitor C1 is charged through
recti
fi
er D1, current-limiting resistor R1, and charge switch S1 to some voltage
V
(meas-
ured through voltmeter M1) in order to store energy
E
fi
2
(C1)
V
2
. When the de
fi
brillation
switch S2 closes, the de
flows through the inductor L1 and the patient,
who has a transthoracic impedance of R
patient
. The discharge waveform depends on the
values of C1, L1, and total impedance (R
inductor
fi
brillation current I
fl
R
patient
). Note that the critical damping
resistance of the circuit is
R
critical
2
L
1
/C
1
. Since de
fi
brillators are commonly designed
assuming that a patient impedance of 50
Ω
, and if we assume an inductor impedance
R
inductor
of 10
Ω
, a suitable R
critical
could be 67
Ω
. The actual energy delivered to a patient
depends on patient impedance and is given by
R
pati
R
en
t
nductor
E
delivered
E
C1
R
patien
t
i
For this example, the discharge is underdamped (biphasic, also referred to as a
Gurvich
waveform
) when the patient resistance is less than about 56
Ω
because
R
patient
R
inductor
56
Ω
10
Ω
66
Ω
R
critical
67
Ω
In this case, the waveform is underdamped and produces a biphasic (oscillating) wave-
form.
If the patient impedance is higher than 67
, the waveform is overdamped (monopha-
sic, also referred to as an
Edmark waveform
). In this case the inductor slows the rate of rise
Ω
Defibrillate
S1
S2
D1
L1
R1
R. Patient
RL1
T1
1
5
Line
V
AC Power
C1
4
8
Neutral
Figure 8.31
Simplified block diagram of a damped sine waveform defibrillator. Transformer T1 steps up the power line voltage to charge
C1 through rectifier D1, R1, and charge switch S1 to some voltage
V
(measured through voltmeter M1) in order to store energy
E
1
2
(C1)
V
2
.
When the defibrillation switch S2 closes, the defibrillation current flows through L1 and the patient.








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search