Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Unfortunately, this preparation inevitably builds up metabolites and electrolytes which
change its electrophysiological characteristics within a few hours of explant. To overcome
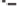
this problem, many investigators [MacLeod et al., 1995] use a second dog to provide cir-
culatory support for the isolated heart, which achieves very stable physiologic conditions
over many hours (Figure 6.37). This preparation makes it possible to regulate coronary
fl
flow rate and blood temperature. In addition, it allows the infusion of cardioactive drugs to
examine the e
ects of physiological change on forward and inverse solutions, since the
support dog eliminates the drugs and their metabolites through its urine output.
This model has a high level of realism, yet maintains adequate control over the relevant
parameters. The tank can be made to have a shape identical to the human torso and can be
instrumented with an almost unlimited number of recording electrodes located both on the
surface and within the volume of the tank. Agarose or conductive polymer “lungs” and
“ribs” can be placed in the tank to simulate volume conductor inhomogenities. The iso-
lated animal heart provides a very realistic and versatile bioelectric source which can be
instrumented and manipulated to mimic many pathologies; for example, burns can be
made on the myocardium to simulate myocardial infarcts.
Despite this
ff
flexibility, the model is not perfect. To start with, there is no autonomic
nervous system present in the isolated heart, so that many responses to external physio-
logical in
fl
uences do not mimic the behavior of a real human heart. In addition, the
mechanical behavior is altered signi
fl
cantly because it hangs freely in the electrolyte with-
out a pericardium or the constraining in
fi
fl
uences of other organs.
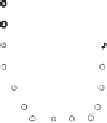
Blood flow
Jugu
l
ar vein
Carotid
artery
Support
dog
Isolated dog heart
Electrodes
Torso-shaped tank
Figure 6.37
An isolated dog heart and human-shaped electrolytic tank have been used for valida-
tion of inverse electrocardiographic methods. This type of preparation uses a second dog to provide
circulatory support for the isolated heart, which achieves very stable physiologic conditions over
many hours.







































































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search