Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Oscilloscope
Isolation
Amplifiers
20pF
1M
CH1
I
20pF
1M
CH2
I
Forearm
1
3
2
Reference
Electrode
1.6
µ
F
1
M
10Vp-p
Isolated
Signal
Generator
100K
I
Figure 6.34
Rosell's method applied to measure electrode-skin impedances using carbon-loaded silicone electrodes: 1, stimulating ring
electrode; 2 and 3, voltage-sensing electrodes. The electrodes are embedded at a depth of 1.5 mm within an isolating silicone rubber cast.
(with a time constant given by R3 and C2) throughout the duration of the stimulation phase of
the FNS pulse to emulate the integration process carried out by the excitable tissue membrane.
After the stimulation phase, the integrated voltage was read through the computer's A/D card.
The actual position of the probe was measured by digitizing the voltage output from the
x
-,
y-
,
and
z
-axis potentiometers linked to the three-dimensional manipulator. The computer reset the
integrator by strobing the RESET line prior to taking a new measurement.
VERY REALISTIC PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNAL SOURCES
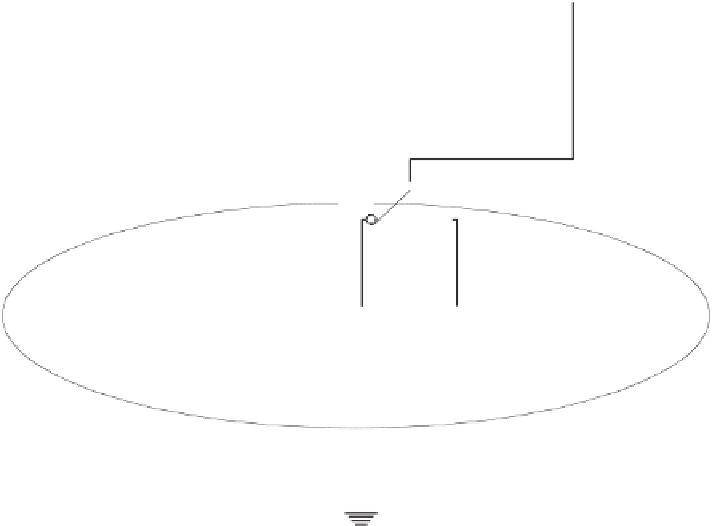
No physical model can really replace the biological realism that can be achieved with an
intact animal model with implanted instrumentation. However, the intact animal presents
the problem that body geometry and exact organ con
cult to inte-
grate as part of an experimental study. A compromise solution is to use an isolated prepa-
ration of the organ generating the biopotentials placed in a synthetic volume conductor that
simulates the human cavity holding the organ.
fi
guration are very di





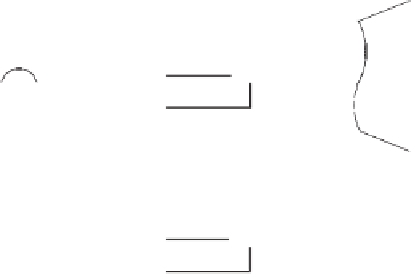




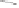





























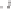
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search