Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 3.1 Spacings (Millimeters) Required to Provide Various Levels of Insulation
between Parts of a Medical Device
Ac Voltage:
125 V
250 V
380 V
Dc Voltage:
150 V
300 V
450 V
Basic insulation (between
Air clearance
1
1.6
2.4
parts of opposite polarity)
Creepage distance
2
3
4
Double or supplementary
Air clearance
1.6
2.5
3.5
insulation
Creepage distance
3
4
6
Double or reinforced
Air clearance
3.2
5
7
Reinforced insulation
Creepage distance
6
8
12
Figure 3.1 and Table 3.1 present a partial view of how to achieve the minimal required
insulation ratings between parts. Although these are only a subset of all possibilities contem-
plated by the standards, they certainly provide a very practical reference for the designer.
LEAKAGE CURRENTS
Evidently, the purpose of the various isolation barriers is to ensure that leakage currents
are maintained within safe values even when a single-fault condition occurs. Three types
of leakage currents are de
fi
ned within the standards:
MEDICAL
INSTRUMENT
Input/Output
Part with
Connection to
Ground
R
S
B
B
AC Power
R
Patient Connections
Floating-Type
Applied Part
Live Part
(Mains Part)
Live Part
B
R
S
Non-Live Part
R
B
Conductive Enclosure
Connected to Protective Ground
Figure 3.1
Some of the requirements for insulation between the parts of a medical instrument. Insulation types: B, basic; S, supplementary;
R, reinforced.

































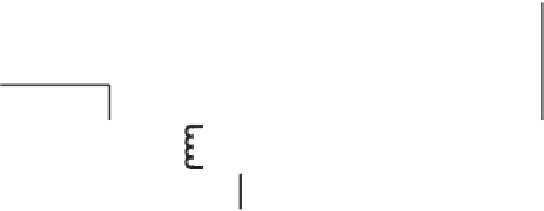




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search