Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
recipient. The blood group is determined by agglutination results of red blood cells reacting with the
corresponding blood serum. The reaction shows the presence of antigens (agglutinogens) on the red
blood cells corresponding to antibodies (agglutinins) in the serum. The sera of anti-A, anti-B, and
anti-AB are obtained from the sera of blood group B persons, A persons, and O persons, respectively.
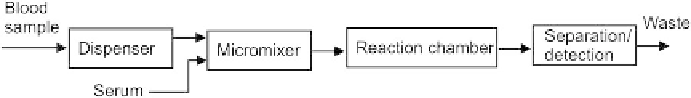
The micromixers work as reactors for the agglutination process. The small size of the device allows
blood typing with a very small sample blood volume on the order of 1
L. Besides the chaotic
micromixers, the reported lab-on-a-chip device also contains flow-splitting microchannels, reaction
chambers, and detection microfilters (
Fig. 9.5
). The blood sample was divided into multiple equal
volumes through the flow-splitting microchannel so that multiple tests can be performed in parallel.
The reaction chambers were used to keep the mixture of the blood and serum for a few minutes
before filtering. The gradually decreasing multistep detection microfilters were designed for separ-
ation of the reacted agglutinated red blood cells. The separation results allow visual detection of
blood groups A, B, and AB.
m
9.2.3
Purification and preconcentration
Sensitive detection is crucial for biochemical analysis. The sample condition may affect the quality of
processes such as polymerase chain reactions (PCR). To improve the accuracy of pathogen detection,
preconcentration and purification of a DNA sample are necessary before PCR. Furthermore, higher
sample concentration also leads to better detection sensitivity. Depending on the filtering or trapping
concept, micromixers can be used for controlling buffer concentration or generating chaotic advection
as described in the following two examples.
Lee et al.
[51]
used a serpentine chaotic micromixer for DNA purification. Because DNA has
a negative charge, it is strongly adsorbed by the glass surface under high-salt buffer conditions. The
binding forces to glass of other contaminants, such as proteins or sugars, are relatively weak. Thus,
packed beads can be used for DNA purification. The adsorbed DNA can subsequently be released and
collected if a low-salt buffer is introduced into the packed chamber. A micromixer can realize the
stepwise change of salt concentration in a buffer solution before flushing it through the packed
chamber. Lee et al. used the micromixer to change the concentration of MgCl
2
from 500 mmol/L to
15 mmol/L. For this purpose, the mixing ratios were controlled at 1:1 and 1:66.
Dielectrophoresis (DEP) can be utilized for trapping, manipulating, and separating bioparticles,
such as virus, DNA molecules, bacteria, and cells. Planar interdigitated electrodes (IDEs) can be
used to generate the nonuniform electric field required for dielectrophoresis. However, the elec-
trophoretic force is only effective if the sample particles are brought close to the surface with the
IDEs, similar to the case of surface-immobilized receptors. Lee and Voldman
[52]
used the
micromixersdepictedinFigs.6.19and6.21tobring more sample particles closer to the IDEs.
FIGURE 9.5
Schematic concept of a lab-on-a-chip for blood typing.




Search WWH ::

Custom Search