Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The
parabolic estimator
assumes a parabolic fitting function for the correlation peak:
Ax
2
f
ð
x
Þ¼
þ
Bx
þ
C
:
(8.19)
In this case, the refined position of the peak is
R
ð
x
1
;
y
Þ
R
ð
x
þ
1
;
y
Þ
x
0
¼
x
þ
Þ
;
2
R
ð
x
1
;
y
Þ
4
R
ð
x
;
y
Þþ
2
R
ð
x
þ
1
;
y
(8.20)
R
ð
x
;
y
1
Þ
R
ð
x
;
y
þ
1
Þ
y
0
¼
y
þ
Þ
:
2
Rðy; x
1
Þ
4
Rðx; yÞþ
2
Rðx; y þ
1
The
Gaussian estimator
assumes a Gaussian distribution of the correlation peak:
C
exp
"
#
2
ð
x
0
x
Þ
f
ð
x
Þ¼
:
(8.21)
k
The position of the peak can the be estimated as
ln
R
ð
x
1
;
y
Þ
ln
R
ð
x
þ
1
;
y
Þ
x
0
¼
x
þ
Þ
;
2ln
R
ð
x
1
;
y
Þ
4ln
R
ð
x
;
y
Þþ
2ln
R
ð
x
þ
1
;
y
(8.22)
ln
R
ð
x
;
y
1
Þ
ln
R
ð
x
;
y
þ
1
Þ
y
0
¼
y
þ
Þ
:
2ln
R
ð
x
;
y
1
Þ
4ln
R
ð
x
;
y
Þþ
2ln
R
ð
x
;
y
þ
1
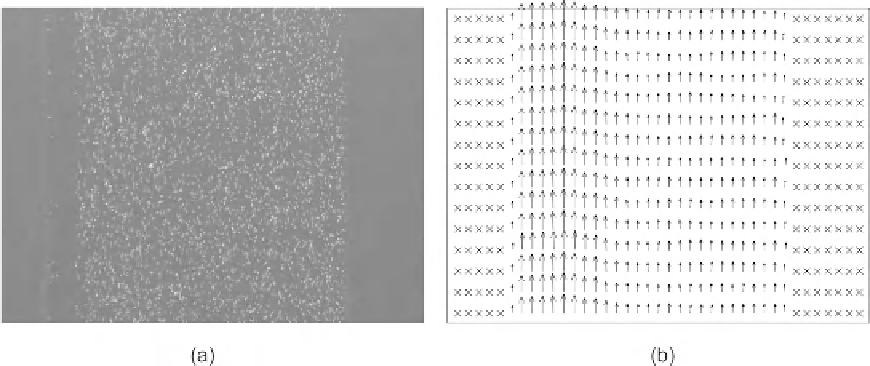
Figure. 8.10
shows a typical particle image and the corresponding evaluated velocity field
(micro-PIV).
The results of micro-PIV can be improved by several techniques, such as removing the background,
improving the particle density, and reducing the noise in the correlation matrix.
FIGURE 8.10
Typical results of a micro-PIV measurement: (a) particle image (single frame, double exposure) and (b) evaluated
velocity field.









Search WWH ::

Custom Search