Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
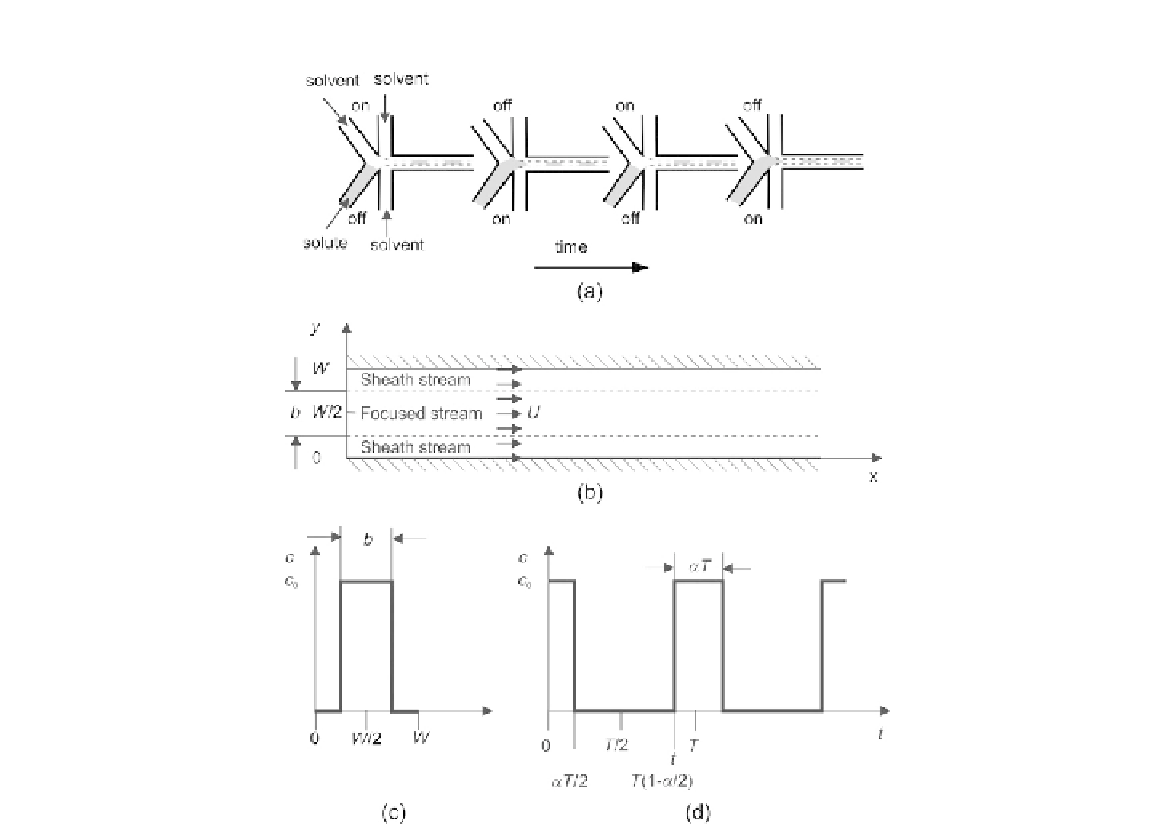
FIGURE 5.16
Mixing in a microchannel based on hydrodynamic focusing and sequential segmentation: (a) the concept; (b) the
two-dimensional model (
x
is the axial direction,
y
is the transversal direction); (c) the boundary condition at
t ¼
0,
x ¼
0; and (d) the transient condition at
x ¼
0,
y ¼W
/2.
where
D
is the molecular diffusion coefficient, which is characteristic for transversal (
y
-axis) diffusion
in our model. The dispersion model
(5.47)
assumes a position far away from the entrance. This
assumption is only true if the position of
x
is long enough for completing diffusion across the channel
height (
x
UH
2
/
D
).
Figure 5.16
(a) shows the two-dimensional model of the mixing concept based on hydrodynamic
focusing and sequential segmentation. Assuming that all the liquids involved in the system have the
same viscosity, the velocity in the mixing channel is uniform across all streams. The focusing ratio
[



Search WWH ::

Custom Search