Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
FIGURE 5.2
Concentration distribution in a parallel lamination micromixer: (a) two streams and (b) three streams.
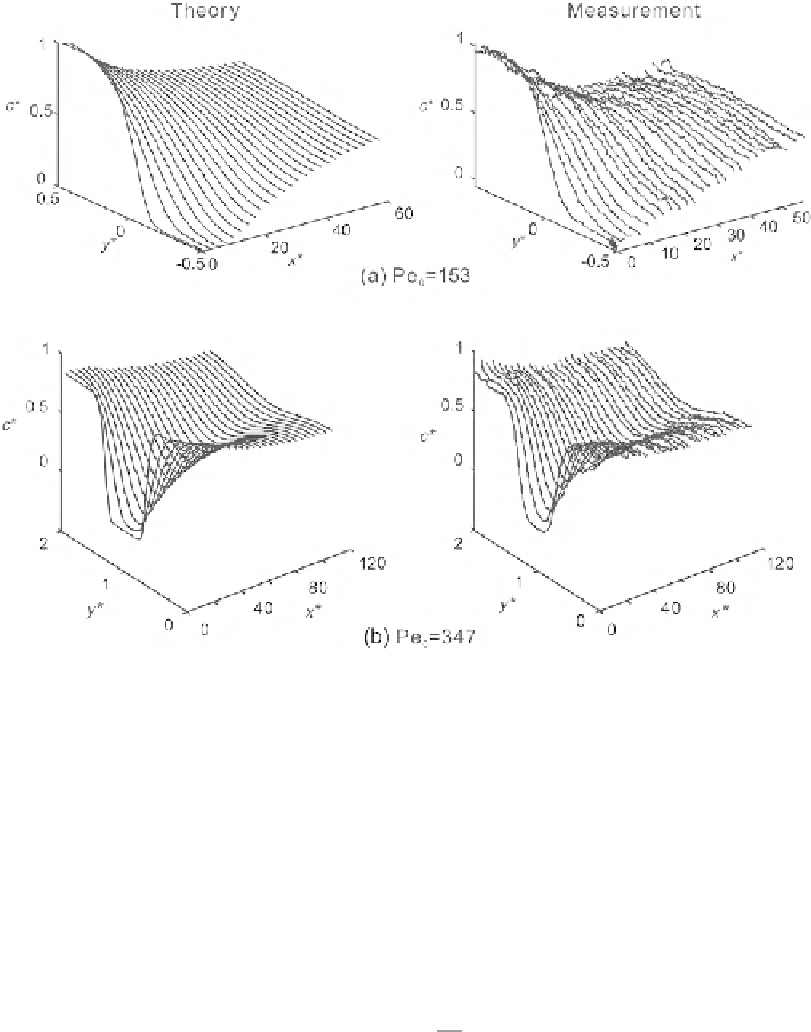
The dispersion effect in parallel lamination is illustrated in
Fig. 5.3
. Due to the no-slip boundary
condition, flow velocity at the channel wall grows from zero to the maximum value at the channel center.
Near the channel wall, molecular diffusion dominates over convective transport, leading to faster
diffusion of the solvent into the solute and a cross-sectional concentration as depicted in
Fig. 5.3
(a). The
dispersion effect can be observed directly with confocal microscopy using Fluo-3 and calcium chloride
(CaCl
2
) solution
[2]
. Fluo-3 is nonfluorescent, but forms with calcium ions into a strongly fluorescent
compound. Ismagilov et al. experimentally observed and, using dimensional analysis toEqn
(5.7)
,derived
the following relation between the broa
de
ning width
d
and other parameters such as axial position
x
,
channel height
H
, and the mean velocity
u
at the channel center and at the channel wall, respectively:
Dx
u
1
2
d
center
ð
x
Þf
DHx
u
1
3
d
wall
ðxÞf
:
(5.8)






Search WWH ::

Custom Search