Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
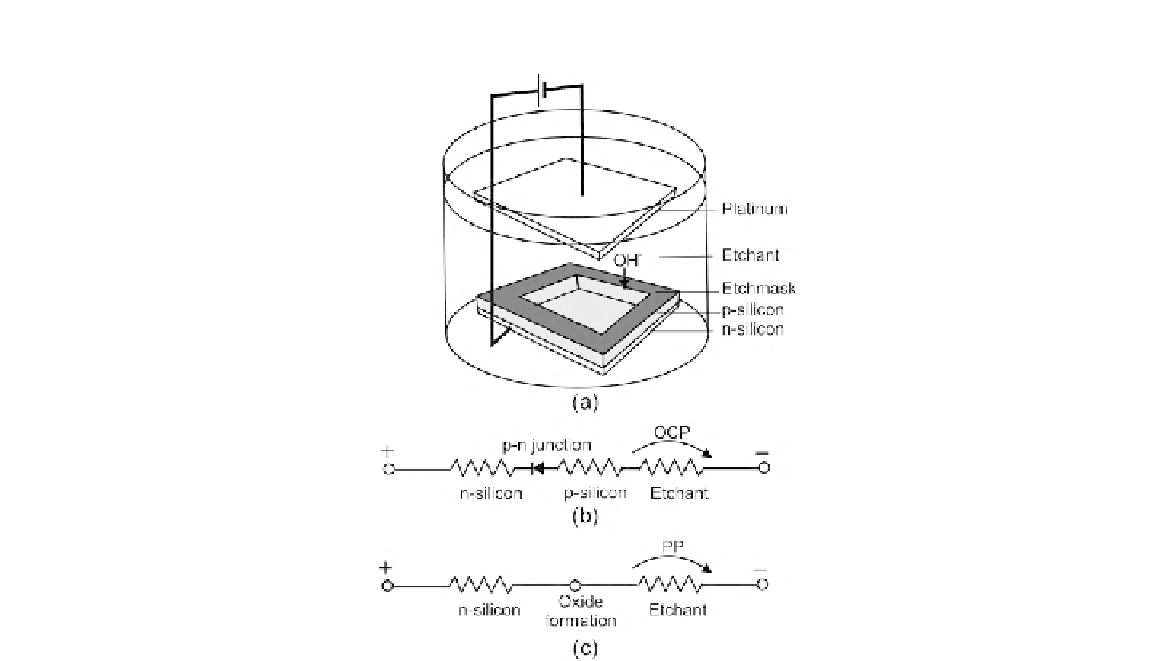
FIGURE 4.3
Electrochemical etch stop: (a) setup; (b) simplified circuit during etching; and (c) simplified circuit at etch stop.
drops to a PP value. The subsequent formation of silicon oxide on the surface automatically stops the
etching process as schematically depicted in
Fig. 4.3
(c).
A further approach of generating holes in silicon is photon pumping. Holes are generated in
positive bias n-silicon by illumination. This technique was utilized for fabricating high-aspect-ratio
structures
[18]
.
4.1.2.2 Dry etching
In dry etching, etchant gases or plasmas remove substrate materials. Generally, dry-etching
techniques are categorized as physical dry etching, chemical dry etching, and physical
chemical
e
etching.
Physical dry etching
utilizes the kinetic energy of particle beams, such as ion beam, electron beam,
or photon beam, to attack the substrate surface. The high-energy particles knock out substrate's atoms
from its surface. The knocked-out material immediately evaporates after leaving the substrate surface.
Since no chemical reaction is involved in this process, almost all materials can be removed by this
technique. The main drawbacks are slow etch rates, low selectivity, and trench effects caused by
reflected ions.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search