Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
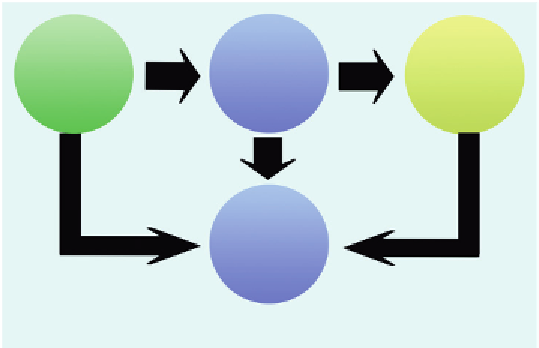
Risk
sensitivity
of others
Behavioral
response of
others
Stimulus
Empathy via
mirror function
Personal
risk
sensitivity
Perception
Perception
Model learning via mirror function
We can recognize examples of model learning in safety issues:
1. During the induction period in a certain job, senior employees can
play the role of safety coach just by acting safely and by vocalizing
their thoughts (thinking aloud) while doing the job. Assimilating
modeled safety issues will be easier if the intention of the expressed
behavior is better understood.
2. When people share narrative experiences (what they have seen,
heard, or experienced while working), these experiences and
connected emotions are planted as an association in the brain of
someone else. The emotional impact of these narrative experiences is
contagious; it jumps from person to person.
3. People will model people in films or videos who could be colleagues
and who display a certain safe procedure if the models are attractive.
The general rule is that a more attractive model leads to stronger
model learning. The higher a model
s perceived status, the stronger the
tendency for others to learn from them. Members of management and
informal leaders within a team have more modeling power compared
to other team members. A second rule is that people follow models for
their actions in combination with their hidden intentions. Fake behav-
ior, in which someone is acting, will not be copied. A third rule is that
people are less sensitive to expressed words from models, as compared
to perceived actions. Words are usually perceived via the conscious
'