Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
become more sophisticated. Most of the activities of the brain happen
autonomously and without any interference from our consciousness.
Modern
brain
Emotional
brain
Basic
brain
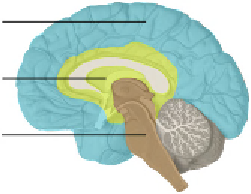
Basic, emotional and modern brain
The systems have a correspondence with certain brain areas, although
no area exclusively hosts one system. In fact, many regions in the modern
brain that are officially designated as the home area of the emotional
brain are also used by the modern brain (Pessoa, 2008; Duncan, 2007).
As far as we can attribute areas to systems, the basic brain is con-
structed out of the spine (the input and output highway of the body),
the brain stem (managing bodily functions like respiration and heart
beat), the hypothalamus
including the pituitary gland, also named
the hypophysis (regulating many functions like day/night rhythm or
sexuality via secretion of hormones), the thalamus (the central control
room, nonconscious perception), and the pineal gland, also named the
epiphysis (regulating sleep) (Kolb, 2008).
—
The emotional brain or limbic system is constructed out of areas
located in the center of the brain around the thalamus, like the amyg-
dala (responsible for anxiety and attraction), the hippocampus (stores
learned information), the gyrus cingularis (safety screening and auto-
biographic archive), and parts of the frontal cortex (labeling feelings).
The modern brain has its main base in the neocortex, the outside
shell of the brain, and is a host of many functions like perception, the
reasoning and executive functions, language, and the motor functions.
The center of reflecting and reasoning is located just above the eyes.
Heavy thinking can even cause a headache in this area.
The pain system is not fully grasped yet. We have pain sensors in
the skin, tissue, muscles, and joints. The pain signals are first analyzed
in the spine. Special cells can generate reflexes to withdraw our body