Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
change a little more into rose, unless red is very convinced of her own
point of view.
Perceiving
each other's
behavior
Perceiving
own behavior
Perceiving
own behavior
Displaying
behavior
Evaluating
behavior
Evaluating
behavior
Displaying
behavior
Intention to
behavior
Intention to
behavior
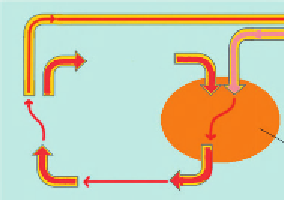
Mirror function
Challenger
Teammate
Challenger influences teammate with different attitude
Concluding, a change of behavior and value system in a team is
possible, but only gradually and with a lot of perseverance. Mirror sys-
tems work like a centrifugal force, bringing the team together in a con-
sensus position in which deviations are only accepted to a limited
degree. Knowing that we constantly have to fight unsafe tendencies,
this creates an extra challenge for those who want to enhance safety.
8.5 THE SCOPE OF MIRRORING
The attractiveness of the model is an indication of the strength of mir-
roring processes. We mirror unless we really dislike the other person,
but how strong is the impact of the model? The rule is that as long as
we can identify with the model, we will adopt behavior, intentions,
aims, and so on. The more we can identify, the more we will automati-
cally mirror.
An interesting question is whether we can identify ourselves with
our superiors. If there is a big difference in communication style and a
big distance (physically or emotionally), we will mirror less. A bossy
boss with a room one floor higher and a lot of air between his door
and his desk will definitely have lower mirroring power than a team
leader who is seen as almost one of the team. The tribe leader has
more authority, but the father of the family more closeness, so also
more mirroring power.
Twenty-five years ago, all teenage girls wanted to be dressed like
Madonna; nowadays the age difference between her and teenagers is