Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
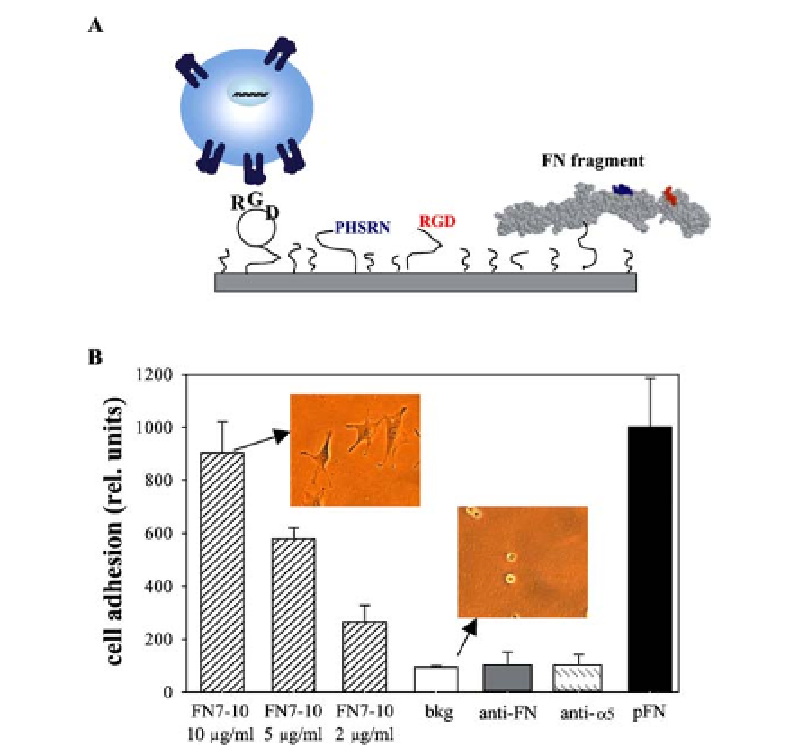
Fig. 5
Second-generation biomimetic adhesive supports.
A
Schematic showing major
strategies pursued to improve integrin binding specificity.
B
A recombinant fragment of
FN (FN7-10) containing the PHSRN and RGD binding sites supports dose-dependent lev-
els of
α
5
β
1
integrin-mediated adhesion. Adhesion levels are comparable to the native
ligand plasma FN (pFN) and are completely blocked by antibodies against the binding
site in FN (anti-FN) or
α
5
β
1
integrin (anti-
α
5
). Adapted from [53, 83]
Non-RGD binding integrins are also critical to many cellular activities and,
thus, represent important targets for therapeutic manipulations. For example,
the collagen-binding integrin
α
2
β
1
regulates various cellular activities, in-
cluding adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation in osteoblasts,
keratinocytes, smooth muscle cells, and platelets [85]. Integrin
α
2
β
1
recog-
nizes the glycine-phenylalanine-hydroxyproline-glycine-glutamate-arginine
(GFOGER) motif in residues 502-507 of the
1[I] chain of COL-I [86]. Inte-
grin recognition is entirely dependent on the triple-helical conformation of
the ligand similar to that of native collagen. Tethering of a triple helical pep-
tide incorporating the GFOGER motif to surfaces promotes
α
α
2
β
1
-mediated
adhesion, focal adhesion signaling, and osteoblast differentiation to levels
comparable to COL-I-coated supports [87, 88]. These results indicate that