Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
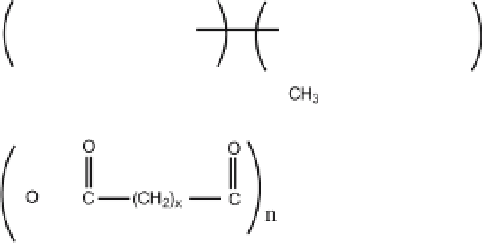
Fig. 2
Chemical structure of
a
poly(lactic acid),
b
poly(glycolic acid),
c
poly(lactic-co-
glycolic) acid,
d
poly(anhydride), and
e
poly(imide)
and bone [66, 67]. In addition to scaffolding, they have also been widely used
for controlled release of drugs [62, 63, 65, 68, 69]. A combination of the above
polymers along with growth factors has successfully been used for guided
bone regeneration in vivo by various investigators [70, 71]. These polymers
possess good mechanical properties and the ester linkages present on the
polymer backbone are labile to hydrolytic degradation. Because of their ex-
cellent mechanical properties, biocompatibility and degradability these poly-
mers, belonging to the poly(
α
-hydroxy acid) family, have also been exploited