Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3
Normal (n=70)
Cancer (n=117)
2
1
0
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
Raman shift (cm
-1
)
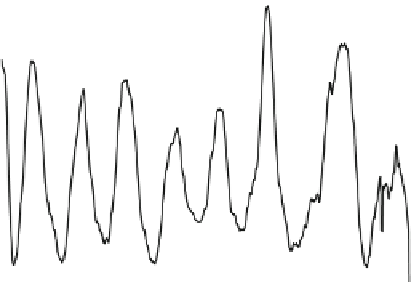
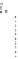
Fig. 1.28
Mean normalized Raman spectra of normal and cancerous laryngeal tissue (Adapted
from Teh et al. [
96
] by permission of the Royal Society of Chemistry)
1.4.8
Other Applications
Raman spectroscopy has also been used for other disease diagnosis. Lau et al.
studied the normal and cancerous laryngeal tissue
in vitro
using NIR Raman
spectroscopy [
95
]. Forty-seven laryngeal specimens were measured (18 normal,
13 carcinoma, and 16 squamous papilloma) with an integration time of 1-30 s
for each spectrum. The normalized Raman spectra of normal and cancerous
laryngeal tissue are shown in Fig.
1.28
. Based on the peak analysis, over 86%
of sensitivity and specificity can be obtained to differentiate normal, carcinoma,
and papilloma. In a recent study, the authors found that classification with random
forest algorithm can yield 88% of sensitivity and 91.4% of specificity for laryngeal
malignancy identification [
96
]. The authors also studied the Raman properties of
normal and cancerous nasopharyngeal tissue
in vitro
[
97
]. Although the sample
size is small (n
D
6), consistent spectral difference was obtained in the three
bands 1;290-1;320 cm
1
, 1;420-1;470 cm
1
,and1;530-1;580 cm
1
.These
in vitro
studies support the potential for future
in vivo
applications in diagnosis of laryngeal
and nasopharynx cancers.
Berger et al. used Raman spectroscopy to measure the concentration of con-
stituents in serum and whole blood
in vitro
[
98
,
99
]. They proposed a PLS model to
predict the concentration of constituents from the Raman spectra of blood. Enejder
et al. measured glucose noninvasively by measuring cutaneous Raman spectra
in vivo
[
100
]. Motz et al. designed a real-time Raman system based on fiber optic
probe (Fig.
1.17
e) and had successfully measured the Raman spectra of human
arteries and breast tissue
in vivo
[
28
,
101
]. Buschman et al. studied coronary


























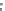



















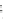





















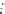

































































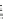





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search