Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
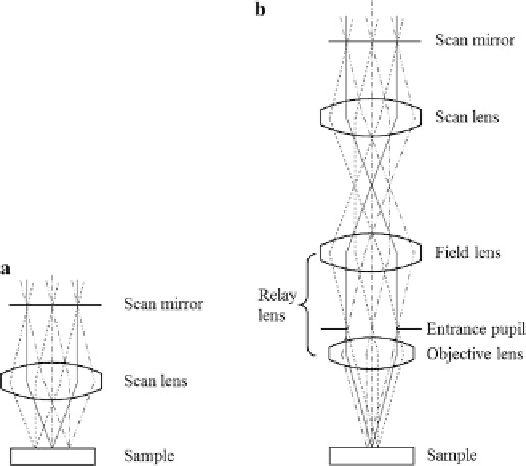
Fig. 9.11
OCT scan lens (
a
) without and (
b
) with relay lens
This section will only discuss the optical design of the sample arm which is the
same for all three types of OCT technique.
9.3.4.1
Scan Lens
Because the OCT system is typically a point scanning system, a scan lens is
needed to scan the focused spot across the sample. Figure
9.11
shows two scan lens
configurations. In Fig.
9.11
a, the scan mirror scans the collimated beam at the pupil
plane, or its conjugated plane, of the scan lens. Ideally, the scan lens should be
an F-theta lens and should be telecentric in the tissue side. The F-theta lens has a
linear relationship between the scan length and the scan angle at the pupil plane.
Good telecentricity is needed for uniform light-collection efficiency and to reduce
post-image processing to correct images at different depths.
Figure
9.11
b is another configuration of the sample arm. A relay lens is used to
relay the focused spot from the scan lens to the sample. This relay lens can also be
treated as the combination of an objective lens and a field lens. The advantage of
this configuration is that the scanning system can be spaced apart from the sample.
It is generally preferable that the OCT system share the same objective lens with
other imaging modalities. The requirement of the scan lens is same as the scan lens
in Fig.
9.11
a.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search