Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Tabl e 8. 2
Examples of images obtained with various endomicroscopic modalities (confocal
fluorescence, reflectance, and two-photon)
Confocal (fluorescence):
a, Image of rectal mucosa; b, Image of descending colon. Both images
acquired after topical application of acriflavine. 1. Goblet cells, 2. Crypt lumen. FOV 500 by
500 m[
12
]
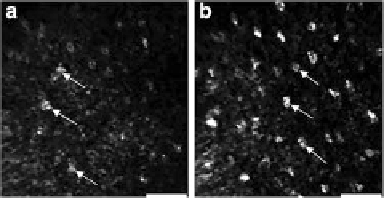
Confocal (reflectance)
: In vivo confocal reflectance images of ventral tongue sites. To emphasize
nuclei acetic acid was topically applied. Nuclei are pointed by arrows. Scale bars: 50 m[
13
]
Multiphoton
: Two-photon fluorescence images of a rat kidney. (a) Surface. (b)-(c) 20- and 40-m
depths. The image size is 475 mby475 m. [
14
]
(0.4-1.0 water) for efficient light collection. In addition to light collection efficiency,
the objective NA also establishes the axial resolution achieved, which can be around
a few microns [
15
,
16
]. (Factors including pinhole size in confocal microscopy as
well as scattering and aberrations within tissue will degrade both axial and lateral
resolution relative to the theoretical values established by wavelength and NA).


Search WWH ::

Custom Search