Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
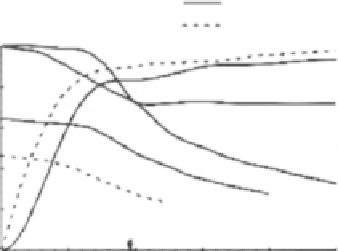
Fig. 6.14
The effect of
changing confocal aperture
half width, measured in
normalized coordinates, on
signal strength, axial
resolution (for a planar
object) and transverse
resolution (for a point object)
for circular or slit apertures
circular aperture
slit aperture
1
signal
0.8
lateral resolution
0.6
axial resolution,
reflection
0.4
axial resolution,
fluorescence
0.2
1st zero Airy disc
0
2
4
6
8
10
V
d
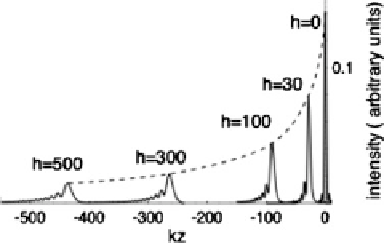
Fig. 6.15
The axial response
in reflection obtained when
an oil-immersion objective is
used to focus a normalized
distance h D kn
s
d inside an
aqueous specimen, refractive
index n
s
.Thevalueh = 500
corresponds to an imaging
depth of 30 m into water
pinhole, the axial resolution is worse, so there does not seem a case for using a slit
from the point of view of signal level. However, it should be remembered that a line
illumination system with a 1-D detector gives a multiplexed signal that images a
complete line of the sample at once, thus greatly increasing detection efficiency for
fast scanning, when performance is limited by saturation of the fluorophore.
6.5.2
Oil and Water Immersion
Axial imaging properties are strongly degraded by the presence of spherical aberra-
tion, which can be introduced when focusing with an oil-immersion objective into
a thick object of refractive index lower than that of the oil. For example, the axial
response in reflection obtained when an oil-immersion objective is used to focus
a normalized distance h
D
kn
S
d inside an aqueous specimen, refractive index n
s
,
is illustrated in Fig.
6.15
.Thevalueh
D
500 corresponds to an imaging depth of
30 m into water. The response becomes broad and asymmetric, with pronounced
side-lobes, and the intensity decreases substantially. For this reason, for live cell
imaging, water immersion objectives are preferable, and most manufacturers now
offer these. The width of the axial response (full width at half-maximum intensity)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search