Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
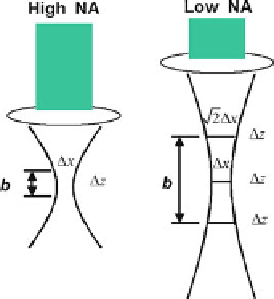
Fig. 5.6
Relationship
between focus spot size and
depth of field for objective
lens with high and low NA
resolution and the imaging depth. A higher lateral resolution leads to a decrease in
the depth of focus, or confocal parameter b, which is twice the Rayleigh range:
x
2
2
2
z
R
D
b
D
:
(5.26)
The Rayleigh range gives the distance from the focal
p
oint to the point where
the light beam diameter has increased by a factor of
p
2. This effectively limits
the scanning range of the OCT, quite apart from the working range of the scanning
reference delay line, as it is the range over which lateral resolution is maintained.
Figure
5.6
shows the relation between the depth of focus (confocal parameter) and
the focused spot size for the objective lens with high and low NA.
5.4.3
Sensitivity
The sensitivity or the optical dynamic range of an OCT system can be defined as
the ratio of the signal power generated by a perfectly reflecting mirror to the noise
of the system and is given by the equation
I
S
I
N
;
SNR
D
(5.27)
where I
S
is the photocurrent at the detector due to the interference term of Eq.
5.18
and which in the case of an ideal 50:50 beam splitter and perfectly reflecting sample
is equal to the total source power P . Therefore, the signal photocurrent can be
expressed as
q
e
„
v
0
P;
I
S
D
(5.28)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search