Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
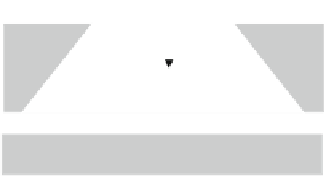
Fig. 4.26
The insulin pump
membrane of nitiol
valve
insulin from
fluid reservoir
delivery
Artificial organs can be mimicked, or their functions can be reconstructed using
very advanced integrated circuits, including micro/nanofluidics. For example, an
artificial pancreas consists of two main parts. A glucose sensor implanted under the
skin will detect the extracellular level and will transmit it to a computer. A drug
delivery capsule having a microfluidic pump, as those described above, will then
deliver the necessary amount of insulin from its reservoir (
Nastruzzi et al. 2005
).
Such an artificial pancreas is already created but still with a limited-in-time function
(
Nastruzzi et al. 2005
). A simple example of an insulin pump is described in
Fig.
4.26
. The film forming the pump takes a dome-like shape when electrically
heated. In this case, insulin from a reservoir is drawn inside the pump and is released
in the delivery tube when the film cools down. The film is termed nitinol and is an
alloy of Ni and Ti (
Schetky et al. 2003
).
A biomimetic microsystem was recently fabricated to reconstitute the critical
functional alveolar capillarity of the human lung (
Huh et al. 2010
). This is a first
step toward organ-on-chip.
References
Ainslie KM, Desai TA (2008) Microfabricated implants for applications in therapeutic delivery,
tissue engineering, and biosensors. Lab on a Chip 8:1864-1878
Bagalkot V, Zhang L, Nissenbaum EL, Jon S, Kantoff PW, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2007)
Quantum dot aptamer conjugates for synchronous cancer imaging, therapy and sensing of drug
delivery based on bi-fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nano Lett 7:3065-3070
Bharadwaj P, Deutsch B, Novotny L (2009) Optical antennas. Adv Optics Photonics 1:438-483
Biondi M, Ungaro F, Quaglia F, Netti PA (2008) Controlled drug delivery in tissue engineering.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:229-242
Boisseau P, Houdy P, Lahmani M (eds) (2010) Nanoscience. nanobiotechnology and nanobiology.
Springer, Berlin
Burke P, Rutherglen C (2010) Towards a single-chip, implantable RFID system: is a single-cell
radio possible? Biomed Microdevices 12:589-596
Charvet G, Rousseau L, Billoint O, Gharbi S, Rostaing J-P, Joucla S, Trevisiol M, Bourgerette
A, Chauvet P, Moulin C, Goy F, Mercier B, Colin M, Spirkovitch S, Fanet H, Meyrand P,
Guillemaud R, Yvert B (2010) BioMEA
TM
: a versatile high-density 3D microelectrode array
system using integrated electronics. Biosensors Bioelectronics 25:1889-1896
Chen X (ed) (2011) Nanoplatform-based molecular imaging, Wiley, New York










Search WWH ::

Custom Search