Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Further heating melts the substance, when the temperature does not rise
with heat due to phase change. So the melting point (T
m
) of the substance is
given by the temperature where dQ/dt
0.
5
13.4 REACTIVITY MEASUREMENTS
This section presents a brief description of derivation of kinetic parameters
from measured data.
13.4.1 Thermogravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) instruments can measure a host of para-
meters like moisture loss, decarboxylation, pyrolysis, loss of solvent, loss of
plasticizer, oxidation, and decomposition for biomass or other substances. It
could also give vital information of the torrefaction of biomass. It also finds
application to determine the carbon content, to compare two similar pro-
ducts, as a quality control tool and for analysis of nanomaterial.
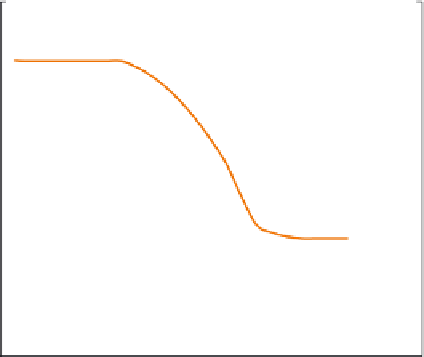
The working of this apparatus is based on the change in mass of the sam-
ple with change in temperature or time (
Figure 13.4
). A typical TGA instru-
ment consists of a pan that rests on a sensitive analytical balance. The test
sample is placed on the pan and is heated externally. A purge gas that may be
reactive or inert (depending on test requirements) is passed over the sample
and exits through the exhaust. The heating rate of the sample can be con-
trolled, and the mass change over the entire period is monitored continuously.
120
2
0
100
-2
80
-4
60
-6
40
-8
20
-10
0
-12
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
Temperature (°C)
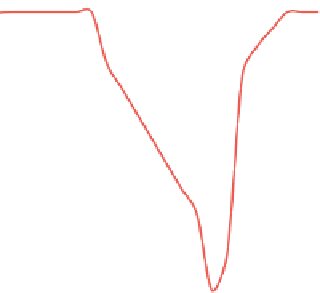
FIGURE 13.4
A TGA curve shows the mass loss percentage and derivative mass loss.












































Search WWH ::

Custom Search