Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Aluminum
scrap
Chute separators
Magnetic block
Biomass
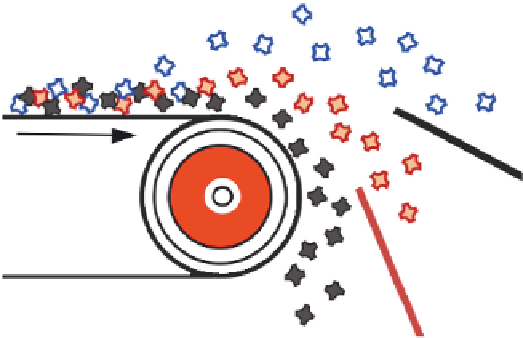
FIGURE 12.11
Separation of nonferrous metals from biomass using eddy current separation.
and classified at the source or at the plant. The following list contains some
of the equipment used for its preliminary sizing along with the typical sizes
produced (Van Loo and Koppejan, 2008, p. 64):
Chunker: 250 to 50 mm
Chipper: 50 to 5 mm
Grinder:
80 mm
,
Pulverizer:
100
μ
m (dust)
,
Different types of equipment are necessary for sizing biomass. One
example is a chunker with multiple blades. Another is a spiral chunker with
a helical cutter mounted on a shaft; as the wood is fed into the machine, the
cutter draws it in and slices it into chunks. The power consumption of a
chunker is relatively low.
Chippers are used to break wood into small pieces. Disc and drum chip-
pers are two common types. In a disc chipper, the wood is fed from the side,
meeting a large disc with several rotating knives. In a drum chipper, several
knives are embedded in grooves (
Figure 12.12
); as the drum rotates, wood
fed at one end is chipped. The chips, which are now uniform in size, are car-
ried away and thrown to the other end by the grooves.
Size-reducing machines consume energy in proportion to the reduction in
size. Chipping typically consumes energy equivalent to 1
3% of the energy
content of the wood (Van Loo and Koppejan, 2008, p. 65).
Grinding is needed when a finer size (
80 mm) of biomass particle is
needed. Hammer mills may be used for this purpose. Where wood is thrown
to the wall of the mill and crushed by hammers. A conventional biomass
combustor or gasifier does not require biomass to be ground to such a fine
size. However, direct cofiring in pulverized coal-fired boilers and the use of
,









Search WWH ::

Custom Search