Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Recycled
flue gas
X.W'
g
,T
go
W
oil
,T''
o
Burner
with
dilution
W
g
,T
gi
W
air
,T'
o
air
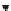
FIGURE 4A.2
Control volume of burner with gas mixing chamber.
where,
A
5
ð
W
v
C
v
1
W
vl
C
g
Þ
T
g0
1
W
t
C
d
T
t
2
W
f
C
b
T
0
1
W
v
L
Oil Burner: Control Volume of Oil Burner
We assume that X fraction of the flue gas leaving the torrefier is fed into the
burner along with fresh air W
air
. Since the recycled gas (XW
0
g
) contains
some unburnt volatiles (XW
vl
), we assume this to supplement oil
in the
burner. We assume fuel oil is preheated to temperature T
v
0
.
Q
vl
5
heat energy released from the combustion of volatile gases
5
XW
vl
LHV
vl
η
where
is combustion efficiency.
From
Figure 4A.2
, we write the energy balance as:
η
XW
0
g
C
g
T
g0
1
W
air
C
a
T
0
0
1
W
g
C
g
T
gi
5
XW
vl
LHV
vl
η
1
W
oil
LHV
η
1
W
oil
C
oil
T
v
0
So, the mass fraction, X, of torrefier product gas recycled is
C
a
T
0
0
2
W
g
C
g
T
gi
αð
A
=
F
Þ
W
oil
LHV
η
2
W
oil
C
oil
T
v
0
X
(A.6)
5
W
0
g
C
g
T
g0
1
W
vl
LHV
vl
η
Substituting values from
Eqs. (A.4)
and
(A.6)
, we have
T
0
0
2
½
W
g
2
W
oil
ðαð
A
=
F
Þ
1
1
Þ
W
g
C
g
T
gi
2
W
oil
αð
A
=
F
Þ
C
a
:
W
oil
LHV
η
2
Woil
C
oil
T
v
0
5
W
0
g
W
0
g
C
g
T
g0
1
W
vl
LHV
vl
η
Amount of oil consumed in the burner is calculated from here as:
1
W
g
W
0
g
C
g
T
gi
C
g
T
g0
1
W
oil
5
P
3
VL
0
fr
LHV
vl
η
2
1
(A.7)
K
2
where,
5
αð
=
Þ
C
a
:
T
0
0
1
η
1
v
0
A
F
LHV
C
oil
T
5
ðα
A
=
F
1
Þ
W
vl
W
0
g
1
and VL
0
fr
5
K
P
;
W
0
g
C
g
T
g0
1
W
0
g
W
vl
LHV
vl
η















Search WWH ::

Custom Search