Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Cold air
Cooled
torrefied
biomass
Torrefield
biomass
Raw
biomass
Dry
biomass
Cooler
Dryer
Torrefier
Warm air
Flue gass
Oil burner
FIGURE 4.10
Schematic of a torrefaction system.
W'
g
,T
go
W
f
,T
o
W
v
W
vl
W
g
Pre-drying
Evaporation
X.W'
g
,T
go
Post-drying
Torrefaction
W
air
,T'
o
W
t
,T
t
Oil burner
W
oil
,T”
o
W
g
,T
gi
FIGURE 4.11
A directly heated integrated torrefaction unit.
an example of a simple torrefaction plant where an oil burner provides the
energy required for the process. For further simplification, we assume that
the volatiles released during torrefaction are not utilized to reduce the oil
consumption.
Design Input
Figure 4.10
shows a schematic of a generic torrefaction unit, while
Figure 4.11
shows an integrated single shaft moving bed reactor that is
directly heated by hot oxygen-free flue gas. The heating medium, hot flue
gas, moves up through the biomass while heating it through gas
particle
convection. Fresh biomass drops from the top of the vertical reactor and des-
cends slowly through the reactor while undergoing different phases of the
process (
Figure 4.11
). Biomass and the heating medium are thus in counter-
current mode.
























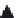






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search