Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
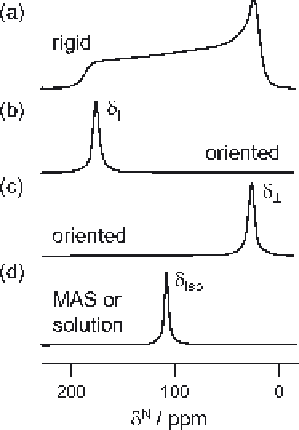
Figure 3.1
Schematic broad-line solid-state NMR spectra for a sample containing a
single backbone amide
15
N label, in which the molecules are: (a)
randomly oriented; (b) uniaxially oriented parallel to the direction of the
applied magnetic field; (c) uniaxially oriented perpendicular to the
direction of the applied magnetic field; and (d) randomly oriented but
spun rapidly at the magic angle.
Slow-spinning solid-state tensor recoupling experiments can recover this lost
information.
9
By defining the orientations of
1
H-
15
N and
1
H-
13
C dipolar
tensors relative to backbone
15
Nand
13
C chemical shift tensors at a majority of
backbone sites in a microcrystalline sample, Rienstra and colleagues recently
generated a highly accurate and precise ensemble of structures for a model
protein, the B1 immunoglobulin-binding domain of streptococcal protein G
(GB1).
10
In solution at room temperature, protein molecules undergo constant
rotational diffusion due to Brownian motion. This continual re-orientation is
typically isotropic and averages away the angular dependence of the chemical
shift in a manner similar to magic-angle spinning (MAS) [Figure 3.1(d)].
Isotropic chemical shifts are affected by the type and oxidation state of the
observed nucleus, its location in a molecule, the orientation of adjacent
covalent bonds, the isotopes of neighbouring nuclei, and proximity to electrons
in aromatic rings and groups with strong magnetic susceptibilities, such as
carbonyl bonds or bound lanthanide ions. However, chemical shift anisotropy
still plays an important role in the relaxation processes of many nuclei,
including protein backbone
13
C9,
15
N and
1
H
N
backbone sites, and the
principal components of these CSTs can be deduced from careful analysis of
auto-correlated and chemical shift anisotropy/dipole-dipole cross-correlated
relaxation rates.
11
Alternatively, scaled-down residual chemical shift aniso-
tropy effects can be reintroduced by performing solution NMR experiments in