Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
spread amongst solid-state NMR groups studying proteins. For DNP applied
to proteins in the solid state, the protein sample is typically doped with
a biradical such as 1-(TEMPO-4-oxy)-3-(TEMPO-4-amino)propan-2-ol
(TOTAPOL, where TEMPO is 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl)
108
as well
as a cryo-protectant, e.g., glycerol. The sample is then cooled to around 80-
100 K for the NMR experiment, during which microwaves from a gyrotron
source are used to irradiate the free electrons on the biradical. Transfer of their
magnetisation to the surrounding protons occurs via the so-called 'cross-
effect'.
109
Since the gyromagnetic ratio of electrons is around 660 times that of
protons, the proton magnetisation can theoretically be enhanced up to 660
times. In practice, the enhancement seen in protein and peptide samples tends
to be closer to 20-120.
107,110-114
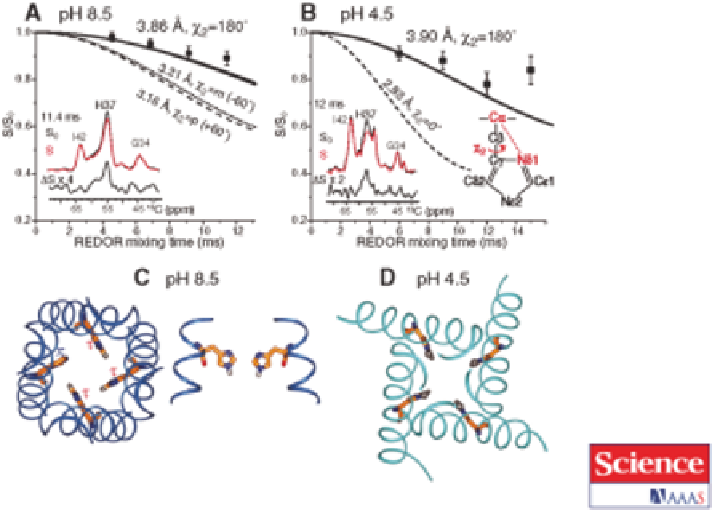
Figure 13.3
Solid-state NMR model for the
15
N,
13
C-labelled M2 influenza proton
selective channel embedded in a cholesterol-containing virus-envelope-
mimetic membrane. The His37 rotameric conformation is determined
from C
a
-N
d1
distances. (A) pH 8.5 data, with representative rotational-
echo double-resonance (REDOR) control (S
0
), dephased (S), and
difference (DS) spectra for the M2 proton channel. The 3.9
˚
distance
indicates x2 5 180u. (B) pH 4.5 data, showing a similar distance and x2
angle. (C) Top- and side-views of the His37 tetrad in the tt rotamer in
the high-pH structure [Protein Data Bank (PDB) number 2KQT] (22).
(D) Top-view of the His37 tetrad in the tt rotamer in the low-pH
structure
(PDB
number:
3C9J).
Reproduced
from
ref.
92
with
permission. # AAAS, 2010.