Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
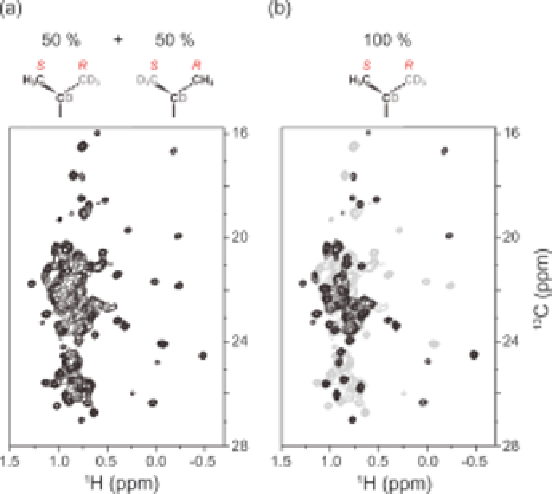
Figure 1.5
Comparison of (
1
H,
13
C) spectra of racemic and stereospecific labelling of
prochiral methyl groups of Leu and Val. Two-dimensional (
1
H,
13
C)
methyl HMQC spectra of TET2 with (a) [U-
2
H;
13
CH
3
,
12
CD
3
]- or (b)
[U-
2
H; proS-
13
CH
3
]-labelled Leu and Val. The spectrum shown in (a) is
also plotted in grey in (b) for comparison. In the molecular fragments
shown above each spectrum, black carbons denote
13
C nuclei; grey
12
C; and D, deuterium.
carbons,
rearrangement of the two methyl groups in 2-acetolactate during leucine/valine
biosynthesis occurs in a stereospecific fashion such that the methyl group
substituent at position-2 becomes the pro-(S) methyl group and carbon-4
becomes the pro-(R) methyl group. A synthetic scheme was reported that
produces [2-
13
CH
3
; 4,4,4-
2
H]-labelled acetolactate. When this molecule is
supplemented into perdeuterated minimal media the pro-(S) methyl groups of
leucine and valine in the over-expressed protein are labelled in a stereospecific
fashion
44
(Figure 1.5). Compared to a-ketoisovalerate, a two-fold gain in
isotopic enrichment can be achieved in the pro-(S) position using 300 mg L
21
of 2-acetolactate with no evidence of isotopic scrambling. Like 2-aceto-2-
hydroxybutyrate, 2-acetolactate is produced as a racemic mixture. Only the 2-
(S)-acetolactate enantiomer is used by E. coli.
1.3 Strategies for Sequence-Specific Resonance
Assignment in High Molecular Weight Proteins
Sequence-specific resonance assignments are a critical prerequisite in
structural, functional and dynamics studies of proteins by NMR spectroscopy.