Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
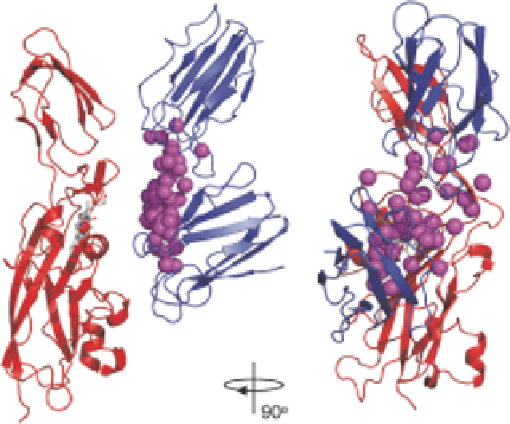
Figure 6.1
Representation of the dynamics in the P. hollandica plastocyanin Y12G/
P14L-cytochrome f complex. Cytochrome f is shown as a red ribbon, the
heme as sticks and the Fe ion as a red sphere. The Cu ions in a set of 50
plastocyanin molecules are shown as magenta spheres. The two most
extreme
orientations
of
plastocyanin
are
shown
as
blue
ribbons.
41
. # American
Reproduced
with
permission
from
ref.
Chemical
Society, 2008.
The mechanism by which PRE occurs depends on the electronic relaxation
rate of the free electrons of the paramagnetic center. For paramagnetic centers
with
a
long
electronic
relaxation
time,
PRE
is
caused
by
dipole-dipole
relaxation (a.k.a. the Solomon mechanism).
77
The simplified relationships
between
the
distance
from
the
electron
to
the
nucleus
(r
IM
)
and
the
longitudinal (R
1,dipole
) or transverse (R
2,dipole
) nuclear
relaxation rate are
shown in eqns (6.3) and (6.4):
8
2
c
I
g
e
m
B
SSz1
R
1,dipole
~
2
15
m
0
4p
3t
c
1zv
I
t
c
ð
Þ
ð
6
:
3
Þ
r
IM
2
c
I
g
e
m
B
SSz1
1
15
m
0
4p
ð
Þ
3t
c
1zv
I
t
c
R
2,dipole
~
4t
c
z
ð
6
:
4
Þ
r
IM
where m
0
is the vacuum permeability, c
I
is the gyromagnetic ratio of nucleus I,
g
e
is the electronic g-factor, m
B
is the Bohr magneton, S is the spin quantum
number of free electrons, v
I
is the Larmor frequency of nucleus I and
t
{
c
~t
{
r
zt
{
s
, where t
r
is the rotational correlation time and t
s
is the
longitudinal electronic relaxation time. Dipole-dipole relaxation is the PRE